diff --git a/README.md b/README.md
index c636328..18fd5e4 100644
--- a/README.md
+++ b/README.md
@@ -1,77 +1,54 @@
-# HW 0: Noisy Planet Part 1 (Intro to Javascript and WebGL)
-
-
-  -
-
-(source: Ken Perlin)
-
-## Objective
-- Check that the tools and build configuration we will be using for the class works.
-- Start learning Typescript and WebGL2
-- Practice implementing noise
-
-## Forking the Code
-Rather than cloning the homework repository, please __fork__ the code into your own repository using the `Fork` button in the upper-right hand corner of the Github UI. This will enable you to have your own personal repository copy of the code, and let you make a live demo (described later in this document).
-
-## Running the Code
-
-1. [Install Node.js](https://nodejs.org/en/download/). Node.js is a JavaScript runtime. It basically allows you to run JavaScript when not in a browser. For our purposes, this is not necessary. The important part is that with it comes `npm`, the Node Package Manager. This allows us to easily declare and install external dependencies such as [dat.GUI](https://workshop.chromeexperiments.com/examples/gui/#1--Basic-Usage), and [glMatrix](http://glmatrix.net/).
-
-2. Using a command terminal, run `npm install` in the root directory of your project. This will download all of those dependencies.
-
-3. Do either of the following (but we highly recommend the first one for reasons we will explain later).
-
- a. Run `npm start` and then go to `localhost:5660` in your web browser
-
- b. Run `npm run build` and then go open `dist/index.html` in your web browser
-
-## Module Bundling
-One of the most important dependencies of our projects is [Webpack](https://webpack.js.org/concepts/). Webpack is a module bundler which allows us to write code in separate files and use `import`s and `export`s to load classes and functions for other files. It also allows us to preprocess code before compiling to a single file. We will be using [Typescript](https://www.typescriptlang.org/docs/home.html) for this course which is Javascript augmented with type annotations. Webpack will convert Typescript files to Javascript files on compilation and in doing so will also check for proper type-safety and usage. Read more about Javascript modules in the resources section below.
-
-## Developing Your Code
-All of the JavaScript code is living inside the `src` directory. The main file that gets executed when you load the page as you may have guessed is `main.ts`. Here, you can make any changes you want, import functions from other files, etc. The reason that we highly suggest you build your project with `npm start` is that doing so will start a process that watches for any changes you make to your code. If it detects anything, it'll automagically rebuild your project and then refresh your browser window for you. Wow. That's cool. If you do it the other way, you'll need to run `npm build` and then refresh your page every time you want to test something.
-
-We would suggest editing your project with Visual Studio Code https://code.visualstudio.com/. Microsoft develops it and Microsoft also develops Typescript so all of the features work nicely together. Sublime Text and installing the Typescript plugins should probably work as well.
-
-## Assignment Details
-1. Take some time to go through the existing codebase so you can get an understanding of syntax and how the code is architected. Much of the code is designed to mirror the class structures used in CIS 460's OpenGL assignments, so it should hopefully be somewhat familiar.
-2. Take a look at the resources linked in the section below. Definitely read about Javascript modules and Typescript. The other links provide documentation for classes used in the code.
-3. Add a `Cube` class that inherits from `Drawable` and at the very least implement a constructor and its `create` function. Then, add a `Cube` instance to the scene to be rendered.
-4. Read the documentation for dat.GUI below. Update the existing GUI in `main.ts` with a parameter to alter the color passed to `u_Color` in the Lambert shader.
-5. Write a custom fragment shader that implements FBM, Worley Noise, or Perlin Noise based on 3D inputs (as opposed to the 2D inputs in the slides). This noise must be used to modify your fragment color. If your custom shader is particularly interesting, you'll earn some bonus points.
-6. Write a custom vertex shader that uses a trigonometric function (e.g. `sin`, `tan`) to non-uniformly modify your cube's vertex positions over time. This will necessitate instantiating an incrementing variable in your Typescript code that you pass to your shader every tick. Refer to the base code's methods of passing variables to shaders if you are unsure how to do so.
-7. Feel free to update any of the files when writing your code. The implementation of the `OpenGLRenderer` is currently very simple.
-
-## Making a Live Demo
-When you push changes to the `master` branch of your repository on Github, a Github workflow will run automatically which builds your code and pushes the build to a new branch `gh-pages`. The configuration file which handles this is located at `.github/workflows/build-and-deploy.yml`. If you want to modify this, you can read more about workflows [here](https://docs.github.com/en/actions/reference/workflow-syntax-for-github-actions).
-
-Once your built code is pushed to `gh-pages`, Github can automatically publish a live site. Configure that by:
-
- 1. Open the Settings tab of your repository in Github.
-
- 2. Scroll down to the Pages tab of the Settings (in the table on the left) and choose which branch to make the source for the deployed project. This should be the `gh-pages` branch which is automatically created after the first successful build of the `master` branch.
-
- 3. Done! Now, any new commits on the `master` branch will be built and pushed to `gh-pages`. The project should be visible at http://username.github.io/repo-name.
-
-
-To check if everything is on the right track:
-
-1. Make sure the `gh-pages` branch of your repo has a files called `index.html`, `bundle.js`, and `bundle.js.map`
-
-2. In the settings tab of the repo, under Pages, make sure it says your site is published at some url.
-
-## Submission
-1. Create a pull request to this repository with your completed code.
-2. Update README.md to contain a solid description of your project with a screenshot of some visuals, and a link to your live demo.
-3. Submit the link to your pull request on Canvas, and add a comment to your submission with a hyperlink to your live demo.
-4. Include a link to your live site.
-
-## Resources
-- Javascript modules https://developer.mozilla.org/en-US/docs/Web/JavaScript/Reference/Statements/import
-- Typescript https://www.typescriptlang.org/docs/home.html
-- dat.gui https://workshop.chromeexperiments.com/examples/gui/
-- glMatrix http://glmatrix.net/docs/
-- WebGL
- - Interfaces https://developer.mozilla.org/en-US/docs/Web/API/WebGL_API
- - Types https://developer.mozilla.org/en-US/docs/Web/API/WebGL_API/Types
- - Constants https://developer.mozilla.org/en-US/docs/Web/API/WebGL_API/Constants
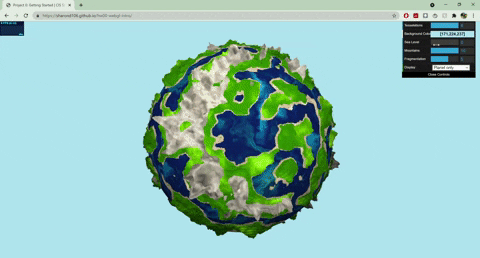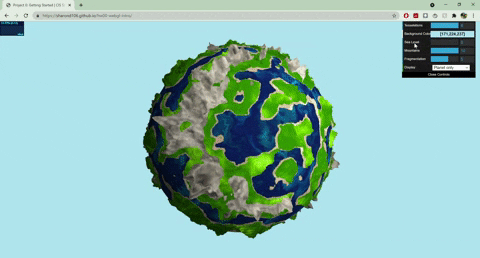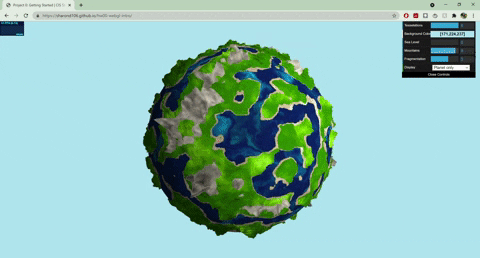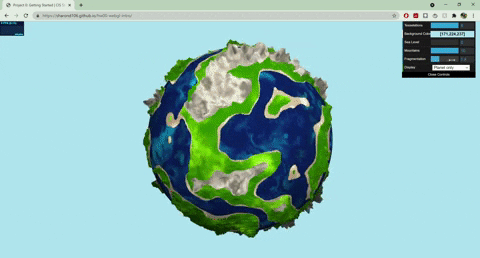
+# HW 1: Noisy Planets
+Sharon Dong (PennKey: sharondo)
+
+Live demo: https://sharond106.github.io/hw00-webgl-intro/
+
+
+
+
+
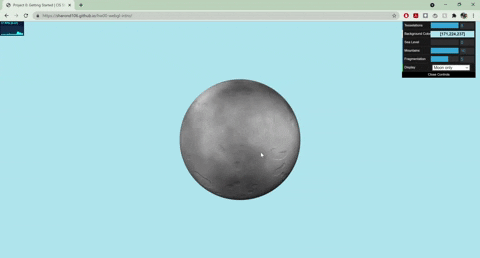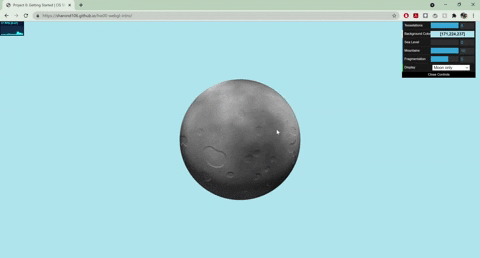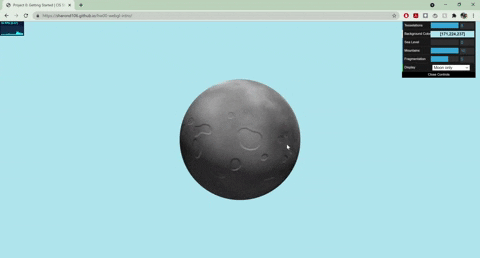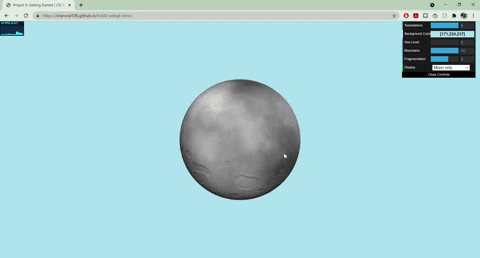
+
+
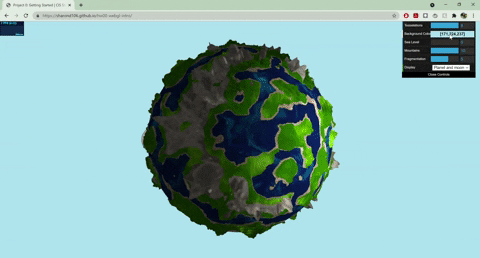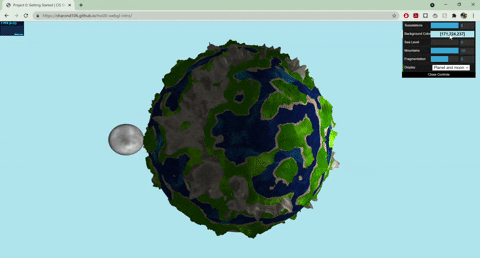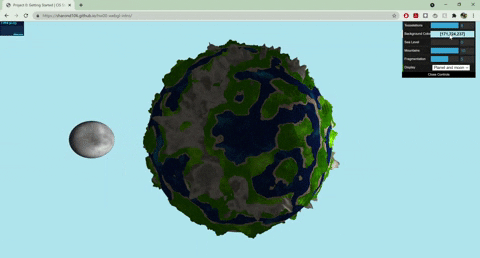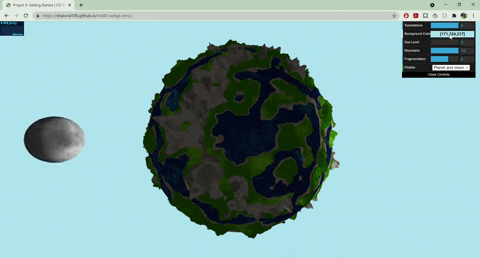
+## Techniques
+- Terrain Placement
+ - The base noise function that determines where the terrain and ocean lie uses worley noise warped with fbm: `color = worley(fbm(p))`
+- Mountains
+ - Terrain created with summed perlin noise at different frequencies: `height = perlin(p) + 0.5*perlin(2*p) + .25*perlin(4*p)`
+ - Colored with a cosine color palette and worley noise warped with fbm
+- Terraces
+ - Terrain created with summed perlin noise at different frequencies
+ - Steps created with a modified sin function: `(perlin + A *sin(B*perlin + C))*f`
+ - Colored with a cosine color palette and fbm
+- Ocean
+ - Colored with a cosine color palette and warped fbm: `color = fbm(p + fbm(p))`
+ - Animated by displacing the input to my fbm noise with time
+ - Blinn phong shading to make white parts look a little snowy
+- Sand
+ - Colored with a cosine color palette and fbm
+ - Blinn phong shading to represent wet sand
+- Moon
+ - Normals displaced with worley noise and a step function to create craters
+ - Rotates around the planet
+ - Colored with fbm
+- Sun
+ - When both planet and moon are displayed, the sun rotates with the moon, and the moon has another light source following it
+ - When only one of the planet/moon is displayed (selected by GUI), the sun moves from left to right, animated with a .75 gain function
+- GUI
+ - Sea level slider changes the threshold of the terrain placement noise value that determines where ocean lies
+ - Mountains slider works similarly
+ - Fragmentation slider changes the frequency of the fbm used for terrain placement
+ - Drop down menu lets you choose between seeing the planet/moon
+- More about the noise functions
+ - All noise functions for my vertex displacements and colors are 3D
+ - My perlin noise and fbm functions use a quintic smooth step function for interpolation
+
+## Helpful Resources I Used
+- https://www.redblobgames.com/maps/terrain-from-noise/
+- https://iquilezles.org/www/articles/warp/warp.htm
+- https://iquilezles.org/www/articles/palettes/palettes.htm
+- https://thebookofshaders.com/edit.php#12/metaballs.frag
+
+# HW 0: Intro to Javascript and WebGL
+The fragment shader is implemented with 3D perlin and worley noise, both displaced with time. You can change one of the base colors using the color picker in the gui on the top right. The vertex shader displaces x and y coordinates with a sin function over time.
+
+
diff --git a/src/geometry/Cube.ts b/src/geometry/Cube.ts
new file mode 100644
index 0000000..e11e741
--- /dev/null
+++ b/src/geometry/Cube.ts
@@ -0,0 +1,91 @@
+import {vec3, vec4} from 'gl-matrix';
+import Drawable from '../rendering/gl/Drawable';
+import {gl} from '../globals';
+
+class Cube extends Drawable {
+ indices: Uint32Array;
+ positions: Float32Array;
+ normals: Float32Array;
+ center: vec4;
+
+ constructor(center: vec3) {
+ super();
+ this.center = vec4.fromValues(center[0], center[1], center[2], 1);
+ }
+
+ create() {
+ this.indices = new Uint32Array([0, 1, 2, 0, 2, 3, //front face
+ 4, 5, 6, 4, 6, 7, // left face
+ 8, 9, 10, 8, 10, 11, // back face
+ 12, 13, 14, 12, 14, 15, // right face
+ 16, 17, 18, 16, 18, 19, // top face
+ 20, 21, 22, 20, 22, 23 // bottom face
+ ]);
+ this.normals = new Float32Array([0, 0, 1, 0, // front face
+ 0, 0, 1, 0,
+ 0, 0, 1, 0,
+ 0, 0, 1, 0,
+ -1, 0, 0, 0, // left face
+ -1, 0, 0, 0,
+ -1, 0, 0, 0,
+ -1, 0, 0, 0,
+ 0, 0, -1, 0, // back face
+ 0, 0, -1, 0,
+ 0, 0, -1, 0,
+ 0, 0, -1, 0,
+ 1, 0, 0, 0, // right face
+ 1, 0, 0, 0,
+ 1, 0, 0, 0,
+ 1, 0, 0, 0,
+ 0, 1, 0, 0, // top face
+ 0, 1, 0, 0,
+ 0, 1, 0, 0,
+ 0, 1, 0, 0,
+ 0, -1, 0, 0, // bottom face
+ 0, -1, 0, 0,
+ 0, -1, 0, 0,
+ 0, -1, 0, 0,
+ ]);
+ this.positions = new Float32Array([-1, -1, 1, 1, // front face
+ 1, -1, 1, 1,
+ 1, 1, 1, 1,
+ -1, 1, 1, 1,
+ -1, -1, -1, 1, // left face
+ -1, -1, 1, 1,
+ -1, 1, 1, 1,
+ -1, 1, -1, 1,
+ 1, -1, -1, 1, //back face
+ -1, -1, -1, 1,
+ -1, 1, -1, 1,
+ 1, 1, -1, 1,
+ 1, -1, 1, 1, // left face
+ 1, -1, -1, 1,
+ 1, 1, -1, 1,
+ 1, 1, 1, 1,
+ -1, 1, 1, 1, // top face
+ 1, 1, 1, 1,
+ 1, 1, -1, 1,
+ -1, 1, -1, 1,
+ -1, -1, -1, 1, // bottom face
+ 1, -1, -1, 1,
+ 1, -1, 1, 1,
+ -1, -1, 1, 1
+ ]);
+ this.generateIdx();
+ this.generatePos();
+ this.generateNor();
+ this.count = this.indices.length;
+ gl.bindBuffer(gl.ELEMENT_ARRAY_BUFFER, this.bufIdx);
+ gl.bufferData(gl.ELEMENT_ARRAY_BUFFER, this.indices, gl.STATIC_DRAW);
+
+ gl.bindBuffer(gl.ARRAY_BUFFER, this.bufNor);
+ gl.bufferData(gl.ARRAY_BUFFER, this.normals, gl.STATIC_DRAW);
+
+ gl.bindBuffer(gl.ARRAY_BUFFER, this.bufPos);
+ gl.bufferData(gl.ARRAY_BUFFER, this.positions, gl.STATIC_DRAW);
+
+ console.log(`Created cube`);
+ }
+};
+
+export default Cube;
diff --git a/src/main.ts b/src/main.ts
index 65a9461..1ce7161 100644
--- a/src/main.ts
+++ b/src/main.ts
@@ -3,6 +3,7 @@ const Stats = require('stats-js');
import * as DAT from 'dat.gui';
import Icosphere from './geometry/Icosphere';
import Square from './geometry/Square';
+import Cube from './geometry/Cube';
import OpenGLRenderer from './rendering/gl/OpenGLRenderer';
import Camera from './Camera';
import {setGL} from './globals';
@@ -11,19 +12,28 @@ import ShaderProgram, {Shader} from './rendering/gl/ShaderProgram';
// Define an object with application parameters and button callbacks
// This will be referred to by dat.GUI's functions that add GUI elements.
const controls = {
- tesselations: 5,
+ tesselations: 8,
'Load Scene': loadScene, // A function pointer, essentially
};
let icosphere: Icosphere;
+let moon: Icosphere;
let square: Square;
-let prevTesselations: number = 5;
+let cube: Cube;
+let prevTesselations: number = 8;
+let prevColor = [171., 224., 237.];
+let time: number = 0;
function loadScene() {
icosphere = new Icosphere(vec3.fromValues(0, 0, 0), 1, controls.tesselations);
icosphere.create();
+ moon = new Icosphere(vec3.fromValues(0, 0, 0), .25, 8.);
+ // moon = new Icosphere(vec3.fromValues(2, 0, 0), .25, 6.);
+ moon.create();
square = new Square(vec3.fromValues(0, 0, 0));
square.create();
+ cube = new Cube(vec3.fromValues(0, 0, 0));
+ cube.create();
}
function main() {
@@ -37,8 +47,28 @@ function main() {
// Add controls to the gui
const gui = new DAT.GUI();
- gui.add(controls, 'tesselations', 0, 8).step(1);
- gui.add(controls, 'Load Scene');
+ gui.add(controls, 'tesselations', 0, 8).step(1).name('Tesselations');
+ // gui.add(controls, 'Load Scene');
+ var color = {
+ color: [171., 224., 237.], // RGB array
+ };
+ gui.addColor(color, 'color').name('Background Color');
+ var sea = {
+ level : 0
+ };
+ gui.add(sea, 'level', 0, 5).name('Sea Level');
+ var terrain = {
+ mountains : 10
+ };
+ gui.add(terrain, 'mountains', 0, 10).name('Mountains');
+ var fragments = {
+ level : 5
+ };
+ gui.add(fragments, 'level', 0, 8).name('Fragmentation');
+ var showObjs = {
+ display : "Planet and moon"
+ }
+ gui.add(showObjs, 'display').options(['Planet and moon', 'Planet only', 'Moon only']).name('Display');
// get canvas and webgl context
const canvas = document.getElementById('canvas');
@@ -53,22 +83,44 @@ function main() {
// Initial call to load scene
loadScene();
- const camera = new Camera(vec3.fromValues(0, 0, 5), vec3.fromValues(0, 0, 0));
+ const camera = new Camera(vec3.fromValues(0, 0, 2.5), vec3.fromValues(0, 0, 0));
const renderer = new OpenGLRenderer(canvas);
- renderer.setClearColor(0.2, 0.2, 0.2, 1);
+ renderer.setClearColor(171. / 255.0, 224. / 255.0, 237. / 255.0, 1);
gl.enable(gl.DEPTH_TEST);
const lambert = new ShaderProgram([
new Shader(gl.VERTEX_SHADER, require('./shaders/lambert-vert.glsl')),
new Shader(gl.FRAGMENT_SHADER, require('./shaders/lambert-frag.glsl')),
]);
+ const noise = new ShaderProgram([
+ new Shader(gl.VERTEX_SHADER, require('./shaders/noise-vert.glsl')),
+ new Shader(gl.FRAGMENT_SHADER, require('./shaders/noise-frag.glsl')),
+ ]);
+ const planet = new ShaderProgram([
+ new Shader(gl.VERTEX_SHADER, require('./shaders/planet-vert.glsl')),
+ new Shader(gl.FRAGMENT_SHADER, require('./shaders/planet-frag.glsl')),
+ ]);
+ const test = new ShaderProgram([
+ new Shader(gl.VERTEX_SHADER, require('./shaders/test-vert.glsl')),
+ new Shader(gl.FRAGMENT_SHADER, require('./shaders/test-frag.glsl')),
+ ]);
+ const moon_lambert = new ShaderProgram([
+ new Shader(gl.VERTEX_SHADER, require('./shaders/moon-vert.glsl')),
+ new Shader(gl.FRAGMENT_SHADER, require('./shaders/moon-frag.glsl')),
+ ]);
// This function will be called every frame
function tick() {
+ time++;
camera.update();
stats.begin();
gl.viewport(0, 0, window.innerWidth, window.innerHeight);
+ if(color.color[0] != prevColor[0] || color.color[1] != prevColor[1] || color.color[2] != prevColor[2])
+ {
+ prevColor = color.color;
+ renderer.setClearColor(color.color[0] / 255.0, color.color[1] / 255.0, color.color[2] / 255.0, 1);
+ }
renderer.clear();
if(controls.tesselations != prevTesselations)
{
@@ -76,10 +128,18 @@ function main() {
icosphere = new Icosphere(vec3.fromValues(0, 0, 0), 1, prevTesselations);
icosphere.create();
}
- renderer.render(camera, lambert, [
- icosphere,
- // square,
- ]);
+
+ if (showObjs.display === "Planet and moon") {
+ renderer.render(camera, [planet, moon_lambert],
+ [icosphere, moon], color.color, time, sea.level, terrain.mountains, fragments.level, true);
+ } else if (showObjs.display === "Planet only") {
+ renderer.render(camera, [planet],
+ [icosphere], color.color, time, sea.level, terrain.mountains, fragments.level, false);
+ } else {
+ renderer.render(camera, [moon_lambert],
+ [moon], color.color, time, sea.level, terrain.mountains, fragments.level, false);
+ }
+
stats.end();
// Tell the browser to call `tick` again whenever it renders a new frame
diff --git a/src/rendering/gl/OpenGLRenderer.ts b/src/rendering/gl/OpenGLRenderer.ts
index 7e527c2..970b2e5 100644
--- a/src/rendering/gl/OpenGLRenderer.ts
+++ b/src/rendering/gl/OpenGLRenderer.ts
@@ -22,19 +22,29 @@ class OpenGLRenderer {
gl.clear(gl.COLOR_BUFFER_BIT | gl.DEPTH_BUFFER_BIT);
}
- render(camera: Camera, prog: ShaderProgram, drawables: Array) {
+ render(camera: Camera, progs: Array, drawables: Array, color: Array,
+ time: number, sea: number, mtn: number, frag: number, display: boolean) {
let model = mat4.create();
let viewProj = mat4.create();
- let color = vec4.fromValues(1, 0, 0, 1);
+ //let color = vec4.fromValues(1, 0, 0, 1);
mat4.identity(model);
mat4.multiply(viewProj, camera.projectionMatrix, camera.viewMatrix);
- prog.setModelMatrix(model);
- prog.setViewProjMatrix(viewProj);
- prog.setGeometryColor(color);
-
- for (let drawable of drawables) {
- prog.draw(drawable);
+ for (let i = 0; i < progs.length; ++i) {
+ let prog = progs[i];
+ prog.setModelMatrix(model);
+ prog.setViewProjMatrix(viewProj);
+ // prog.setGeometryColor(vec4.fromValues(color[0]/255, color[1]/255, color[2]/255, 1));
+ prog.setTime(time);
+ prog.setCamPos(vec4.fromValues(camera.position[0], camera.position[1], camera.position[2], 1.));
+ prog.setSea(sea);
+ prog.setMountains(mtn);
+ prog.setFragments(frag);
+ prog.draw(drawables[i]);
+ if (display)
+ prog.setPlanetAndMoon(1.);
+ else
+ prog.setPlanetAndMoon(0.);
}
}
};
diff --git a/src/rendering/gl/ShaderProgram.ts b/src/rendering/gl/ShaderProgram.ts
index 67fef40..157627f 100644
--- a/src/rendering/gl/ShaderProgram.ts
+++ b/src/rendering/gl/ShaderProgram.ts
@@ -29,6 +29,12 @@ class ShaderProgram {
unifModelInvTr: WebGLUniformLocation;
unifViewProj: WebGLUniformLocation;
unifColor: WebGLUniformLocation;
+ unifTime: WebGLUniformLocation;
+ unifCamPos: WebGLUniformLocation;
+ unifSeaLevel: WebGLUniformLocation;
+ unifMountains: WebGLUniformLocation;
+ unifFragments: WebGLUniformLocation;
+ unifPlanetAndMoon: WebGLUniformLocation;
constructor(shaders: Array) {
this.prog = gl.createProgram();
@@ -48,6 +54,12 @@ class ShaderProgram {
this.unifModelInvTr = gl.getUniformLocation(this.prog, "u_ModelInvTr");
this.unifViewProj = gl.getUniformLocation(this.prog, "u_ViewProj");
this.unifColor = gl.getUniformLocation(this.prog, "u_Color");
+ this.unifTime = gl.getUniformLocation(this.prog, "u_Time");
+ this.unifCamPos = gl.getUniformLocation(this.prog, "u_CameraPos");
+ this.unifSeaLevel = gl.getUniformLocation(this.prog, "u_Sea");
+ this.unifMountains = gl.getUniformLocation(this.prog, "u_Mountains");
+ this.unifFragments = gl.getUniformLocation(this.prog, "u_Fragments");
+ this.unifPlanetAndMoon = gl.getUniformLocation(this.prog, "u_PlanetAndMoon");
}
use() {
@@ -85,6 +97,48 @@ class ShaderProgram {
}
}
+ setTime(time: number) {
+ this.use();
+ if (this.unifTime !== -1) {
+ gl.uniform1i(this.unifTime, time);
+ }
+ }
+
+ setCamPos(pos: vec4) {
+ this.use();
+ if (this.unifCamPos !== -1) {
+ gl.uniform4fv(this.unifCamPos, pos);
+ }
+ }
+
+ setSea(sea: number) {
+ this.use();
+ if(this.unifSeaLevel != -1) {
+ gl.uniform1f(this.unifSeaLevel, sea);
+ }
+ }
+
+ setMountains(mtn: number) {
+ this.use();
+ if(this.unifMountains != -1) {
+ gl.uniform1f(this.unifMountains, mtn);
+ }
+ }
+
+ setFragments(frag: number) {
+ this.use();
+ if(this.unifFragments != -1) {
+ gl.uniform1f(this.unifFragments, frag);
+ }
+ }
+
+ setPlanetAndMoon(x: number) {
+ this.use();
+ if(this.unifPlanetAndMoon != -1) {
+ gl.uniform1f(this.unifPlanetAndMoon, x);
+ }
+ }
+
draw(d: Drawable) {
this.use();
diff --git a/src/shaders/lambert-frag.glsl b/src/shaders/lambert-frag.glsl
index 2b8e11b..10bb4ff 100644
--- a/src/shaders/lambert-frag.glsl
+++ b/src/shaders/lambert-frag.glsl
@@ -30,7 +30,7 @@ void main()
// Calculate the diffuse term for Lambert shading
float diffuseTerm = dot(normalize(fs_Nor), normalize(fs_LightVec));
// Avoid negative lighting values
- // diffuseTerm = clamp(diffuseTerm, 0, 1);
+ diffuseTerm = clamp(diffuseTerm, 0.f, 1.f);
float ambientTerm = 0.2;
diff --git a/src/shaders/moon-frag.glsl b/src/shaders/moon-frag.glsl
new file mode 100644
index 0000000..86c8a2f
--- /dev/null
+++ b/src/shaders/moon-frag.glsl
@@ -0,0 +1,98 @@
+#version 300 es
+
+// This is a fragment shader. If you've opened this file first, please
+// open and read lambert.vert.glsl before reading on.
+// Unlike the vertex shader, the fragment shader actually does compute
+// the shading of geometry. For every pixel in your program's output
+// screen, the fragment shader is run for every bit of geometry that
+// particular pixel overlaps. By implicitly interpolating the position
+// data passed into the fragment shader by the vertex shader, the fragment shader
+// can compute what color to apply to its pixel based on things like vertex
+// position, light position, and vertex color.
+precision highp float;
+
+uniform vec4 u_Color; // The color with which to render this instance of geometry.
+
+// These are the interpolated values out of the rasterizer, so you can't know
+// their specific values without knowing the vertices that contributed to them
+in vec4 fs_Nor;
+in vec4 fs_Pos;
+in vec4 fs_LightVec;
+in vec4 fs_Col;
+
+out vec4 out_Col; // This is the final output color that you will see on your
+ // screen for the pixel that is currently being processed.
+float random1( vec3 p ) {
+ return fract(sin((dot(p, vec3(127.1,
+ 311.7,
+ 191.999)))) *
+ 18.5453);
+}
+
+float smootherStep(float a, float b, float t) {
+ t = t*t*t*(t*(t*6.0 - 15.0) + 10.0);
+ return mix(a, b, t);
+}
+
+float interpNoise3D(float x, float y, float z) {
+ x *= 2.;
+ y *= 2.;
+ z *= 2.;
+ float intX = floor(x);
+ float fractX = fract(x);
+ float intY = floor(y);
+ float fractY = fract(y);
+ float intZ = floor(z);
+ float fractZ = fract(z);
+ float v1 = random1(vec3(intX, intY, intZ));
+ float v2 = random1(vec3(intX + 1., intY, intZ));
+ float v3 = random1(vec3(intX, intY + 1., intZ));
+ float v4 = random1(vec3(intX + 1., intY + 1., intZ));
+
+ float v5 = random1(vec3(intX, intY, intZ + 1.));
+ float v6 = random1(vec3(intX + 1., intY, intZ + 1.));
+ float v7 = random1(vec3(intX, intY + 1., intZ + 1.));
+ float v8 = random1(vec3(intX + 1., intY + 1., intZ + 1.));
+
+ float i1 = smootherStep(v1, v2, fractX);
+ float i2 = smootherStep(v3, v4, fractX);
+ float result1 = smootherStep(i1, i2, fractY);
+ float i3 = smootherStep(v5, v6, fractX);
+ float i4 = smootherStep(v7, v8, fractX);
+ float result2 = smootherStep(i3, i4, fractY);
+ return smootherStep(result1, result2, fractZ);
+}
+
+float fbm(float x, float y, float z) {
+ float total = 0.;
+ float persistence = 0.5f;
+ float octaves = 6.;
+ for(float i = 1.; i <= octaves; i++) {
+ float freq = pow(2., i);
+ float amp = pow(persistence, i);
+ total += interpNoise3D(x * freq, y * freq, z * freq) * amp;
+ }
+ return total;
+}
+
+void main()
+{
+ // Material base color (before shading)
+ vec4 diffuseColor = vec4(.5, .5, .5, 1);
+
+ // Calculate the diffuse term for Lambert shading
+ float diffuseTerm = dot(normalize(fs_Nor), normalize(fs_LightVec));
+ // Avoid negative lighting values
+ diffuseTerm = clamp(diffuseTerm, 0.f, 1.f);
+
+ float ambientTerm = 0.2;
+
+ float lightIntensity = diffuseTerm + ambientTerm; //Add a small float value to the color multiplier
+ //to simulate ambient lighting. This ensures that faces that are not
+ //lit by our point light are not completely black.
+ float f = fbm(fs_Pos.x, fs_Pos.y, fs_Pos.z);
+
+ // Compute final shaded color
+ out_Col = vec4(vec3(clamp(f * 1.2 * lightIntensity, 0., .9)), 1);
+ // out_Col = vec4((fs_Nor.xyz + vec3(1.)) * 0.5, 1.);
+}
diff --git a/src/shaders/moon-vert.glsl b/src/shaders/moon-vert.glsl
new file mode 100644
index 0000000..fd55fd6
--- /dev/null
+++ b/src/shaders/moon-vert.glsl
@@ -0,0 +1,150 @@
+#version 300 es
+
+//This is a vertex shader. While it is called a "shader" due to outdated conventions, this file
+//is used to apply matrix transformations to the arrays of vertex data passed to it.
+//Since this code is run on your GPU, each vertex is transformed simultaneously.
+//If it were run on your CPU, each vertex would have to be processed in a FOR loop, one at a time.
+//This simultaneous transformation allows your program to run much faster, especially when rendering
+//geometry with millions of vertices.
+
+uniform mat4 u_Model; // The matrix that defines the transformation of the
+ // object we're rendering. In this assignment,
+ // this will be the result of traversing your scene graph.
+
+uniform mat4 u_ModelInvTr; // The inverse transpose of the model matrix.
+ // This allows us to transform the object's normals properly
+ // if the object has been non-uniformly scaled.
+
+uniform mat4 u_ViewProj; // The matrix that defines the camera's transformation.
+ // We've written a static matrix for you to use for HW2,
+ // but in HW3 you'll have to generate one yourself
+uniform int u_Time;
+uniform float u_PlanetAndMoon;
+
+in vec4 vs_Pos; // The array of vertex positions passed to the shader
+
+in vec4 vs_Nor; // The array of vertex normals passed to the shader
+
+in vec4 vs_Col; // The array of vertex colors passed to the shader.
+
+out vec4 fs_Nor; // The array of normals that has been transformed by u_ModelInvTr. This is implicitly passed to the fragment shader.
+out vec4 fs_LightVec; // The direction in which our virtual light lies, relative to each vertex. This is implicitly passed to the fragment shader.
+out vec4 fs_Col; // The color of each vertex. This is implicitly passed to the fragment shader.
+out vec4 fs_Pos;
+
+
+vec3 random3(vec3 p) {
+ return fract(sin(vec3(dot(p,vec3(127.1, 311.7, 191.999)),
+ dot(p,vec3(269.5, 183.3, 765.54)),
+ dot(p, vec3(420.69, 631.2,109.21))))
+ *43758.5453);
+}
+
+float worley(vec3 p) {
+ p *= 20.;
+ vec3 pInt = floor(p);
+ vec3 pFract = fract(p);
+ float minDist = 1.0;
+ for (int x = -1; x <= 1; x++) {
+ for (int y = -1; y <= 1; y++) {
+ for (int z = -1; z <= 1; z++) {
+ vec3 neighbor = vec3(float(x), float(y), float(z));
+ vec3 voronoi = random3(pInt + neighbor);
+ vec3 diff = neighbor + voronoi - pFract;
+ float dist = length(diff);
+ minDist = min(minDist, dist*minDist);
+ }
+ }
+ }
+ return minDist;
+}
+
+
+vec3 cartesian(float r, float theta, float phi) {
+ return vec3(r * sin(phi) * cos(theta),
+ r * sin(phi) * sin(theta),
+ r * cos(phi));
+}
+
+// output is vec3(radius, theta, phi)
+vec3 polar(vec4 p) {
+ float r = sqrt(p.x * p.x + p.y * p.y + p.z * p.z);
+ float theta = atan(p.y / p.x);
+ float phi = acos(p.z / sqrt(p.x * p.x + p.y * p.y + p.z * p.z));
+ return vec3(r, theta, phi);
+}
+
+vec4 transformToWorld(vec4 nor) {
+ vec3 normal = normalize(vec3(vs_Nor));
+ vec3 tangent = normalize(cross(vec3(0.0, 1.0, 0.0), normal));
+ vec3 bitangent = normalize(cross(normal, tangent));
+ mat4 transform;
+ transform[0] = vec4(tangent, 0.0);
+ transform[1] = vec4(bitangent, 0.0);
+ transform[2] = vec4(normal, 0.0);
+ transform[3] = vec4(0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 1.0);
+ return vec4(normalize(vec3(transform * nor)), 0.0);
+}
+
+vec4 worleyNormal(vec4 p) {
+ vec3 polars = polar(p);
+ float offset = .01;
+ vec3 xNeg = cartesian(polars.x, polars.y - offset, polars.z);
+ vec3 xPos = cartesian(polars.x, polars.y + offset, polars.z);
+ vec3 yNeg = cartesian(polars.x, polars.y, polars.z - offset);
+ vec3 yPos = cartesian(polars.x, polars.y, polars.z + offset);
+ float xNegNoise = step(.12, worley(xNeg)) * .02;
+ float xPosNoise = step(.12, worley(xPos)) * .02;
+ float yNegNoise = step(.12, worley(yNeg)) * .02;
+ float yPosNoise = step(.12, worley(yPos)) * .02;
+
+ float xDiff = (xPosNoise - xNegNoise) * 10.;
+ float yDiff = (yPosNoise - yNegNoise) * 10.;
+ p.z = sqrt(1. - xDiff * xDiff - yDiff * yDiff);
+ return vec4(vec3(xDiff, yDiff, p.z), 0);
+}
+
+float GetBias(float time, float bias)
+{
+ return (time / ((((1.0/bias) - 2.0)*(1.0 - time))+1.0));
+}
+
+float GetGain(float time, float gain)
+{
+ if(time < 0.5)
+ return GetBias(time * 2.0,gain)/2.0;
+ else
+ return GetBias(time * 2.0 - 1.0,1.0 - gain)/2.0 + 0.5;
+}
+
+void main()
+{
+ fs_Col = vs_Col; // Pass the vertex colors to the fragment shader for interpolation
+
+ mat3 invTranspose = mat3(u_ModelInvTr);
+
+ vec4 pos;
+ vec4 lightPos;
+ if (u_PlanetAndMoon > 0.) {
+ float angle = .01 * float(u_Time);
+ vec4 col0 = vec4(cos(angle), 0, -1.*sin(angle), 0);
+ vec4 col1 = vec4(0, 1, 0, 0);
+ vec4 col2 = vec4(sin(angle), 0, cos(angle), 0);
+ vec4 col3 = vec4(0, 0, 0, 1);
+ mat4 rotate = mat4(col0, col1, col2, col3);
+ pos = rotate * (vs_Pos + vec4(2., 0., 0., 0.));
+ lightPos = rotate * vec4(10, 0, 0, 1);
+ } else {
+ pos = vs_Pos;
+ lightPos = mix(vec4(10., 4., 10., 1.), vec4(-10., 4., 10., 1.), GetGain((sin(float(u_Time)*.01) + 1.)/2., .75));
+ }
+
+ vec4 modelposition = u_Model * pos;
+ fs_Pos = vs_Pos;
+ fs_Nor = transformToWorld(normalize(worleyNormal(vs_Pos)));
+
+ fs_LightVec = lightPos - modelposition; // Compute the direction in which the light source lies
+
+ gl_Position = u_ViewProj * modelposition;// gl_Position is a built-in variable of OpenGL which is
+ // used to render the final positions of the geometry's vertices
+}
diff --git a/src/shaders/noise-frag.glsl b/src/shaders/noise-frag.glsl
new file mode 100644
index 0000000..81bbd64
--- /dev/null
+++ b/src/shaders/noise-frag.glsl
@@ -0,0 +1,91 @@
+#version 300 es
+
+precision highp float;
+
+uniform vec4 u_Color;
+uniform highp int u_Time;
+
+in vec4 fs_Pos;
+in vec4 fs_Nor;
+in vec4 fs_LightVec;
+in vec4 fs_Col;
+
+out vec4 out_Col;
+
+// Returns random vec3 in range [0, 1]
+vec3 random3(vec3 p) {
+ return fract(sin(vec3(dot(p,vec3(127.1, 311.7, 191.999)),
+ dot(p,vec3(269.5, 183.3, 765.54)),
+ dot(p, vec3(420.69, 631.2,109.21))))
+ *43758.5453);
+}
+
+// Returns a surflet
+float surflet(vec3 p, vec3 corner) {
+ vec3 t = abs(p - corner);
+ vec3 falloff = vec3(1.f) - 6.f * vec3(pow(t.x, 5.f),pow(t.y, 5.f), pow(t.z, 5.f))
+ + 15.f * vec3(pow(t.x, 4.f), pow(t.y, 4.f),pow(t.z, 4.f))
+ - 10.f * vec3(pow(t.x, 3.f), pow(t.y, 3.f),pow(t.z, 3.f));
+ vec3 gradient = random3(corner) * 2.f - vec3(sin(0.02 * float(u_Time)) + 1.f);
+ vec3 dist = p - corner;
+ float dotProd = dot(dist, gradient);
+ return dotProd * falloff.x * falloff.y * falloff.z;
+}
+
+float perlin(vec3 p) {
+ p = p * 1.5;
+ float surfletSum = 0.f;
+ for (int dx = 0; dx <= 1; dx++) {
+ for (int dy = 0; dy <= 1; dy++) {
+ for (int dz = 0; dz <= 1; dz++) {
+ surfletSum += surflet(p, vec3(floor(p.x), floor(p.y), floor(p.z)) + vec3(dx, dy, dz));
+ }
+ }
+ }
+ return surfletSum;
+}
+
+float worley(vec3 p) {
+ p *= 1.5;
+ vec3 pInt = floor(p);
+ vec3 pFract = fract(p);
+ float minDist = 1.0;
+ for (int x = -1; x <= 1; x++) {
+ for (int y = -1; y <= 1; y++) {
+ for (int z = -1; z <= 1; z++) {
+ vec3 neighbor = vec3(float(x), float(y), float(z));
+ vec3 voronoi = random3(pInt + neighbor);
+ voronoi = 0.5 + 0.5 * sin(0.1 * float(u_Time) + 13.2831 * voronoi);
+ vec3 diff = neighbor + voronoi - pFract;
+ float dist = length(diff);
+ minDist = min(minDist, dist);
+ }
+ }
+ }
+ return minDist;
+}
+
+void main()
+{
+ vec4 diffuseColor = u_Color;
+
+ // Calculate the diffuse term for Lambert shading
+ float diffuseTerm = dot(normalize(fs_Nor), normalize(fs_LightVec));
+ // Avoid negative lighting values
+ diffuseTerm = clamp(diffuseTerm, 0.f, 1.f);
+
+ float ambientTerm = 0.2;
+
+ float lightIntensity = diffuseTerm + ambientTerm; //Add a small float value to the color multiplier
+ //to simulate ambient lighting. This ensures that faces that are not
+ //lit by our point light are not completely black.
+ float perlinNoise = perlin(vec3(fs_Pos));
+ vec3 a = vec3(u_Color);
+ vec3 b = vec3(0.688, 0.558, 0.500);
+ vec3 c = vec3(255.0 / 255.0, 244.0 / 255.0, 224.0 / 255.0);
+ vec3 d = vec3(0.588, -0.342, 0.048);
+ vec3 perlinColor = a + b * cos(6.28 * worley(vec3(fs_Pos)) * perlinNoise * 4. * c + d);
+
+ // Compute final shaded color
+ out_Col = vec4(perlinColor.rgb * lightIntensity, diffuseColor.a);
+}
diff --git a/src/shaders/noise-vert.glsl b/src/shaders/noise-vert.glsl
new file mode 100644
index 0000000..9d6bf15
--- /dev/null
+++ b/src/shaders/noise-vert.glsl
@@ -0,0 +1,59 @@
+#version 300 es
+
+//This is a vertex shader. While it is called a "shader" due to outdated conventions, this file
+//is used to apply matrix transformations to the arrays of vertex data passed to it.
+//Since this code is run on your GPU, each vertex is transformed simultaneously.
+//If it were run on your CPU, each vertex would have to be processed in a FOR loop, one at a time.
+//This simultaneous transformation allows your program to run much faster, especially when rendering
+//geometry with millions of vertices.
+
+uniform mat4 u_Model; // The matrix that defines the transformation of the
+ // object we're rendering. In this assignment,
+ // this will be the result of traversing your scene graph.
+
+uniform mat4 u_ModelInvTr; // The inverse transpose of the model matrix.
+ // This allows us to transform the object's normals properly
+ // if the object has been non-uniformly scaled.
+
+uniform mat4 u_ViewProj; // The matrix that defines the camera's transformation.
+ // We've written a static matrix for you to use for HW2,
+ // but in HW3 you'll have to generate one yourself
+uniform highp int u_Time;
+
+in vec4 vs_Pos; // The array of vertex positions passed to the shader
+
+in vec4 vs_Nor; // The array of vertex normals passed to the shader
+
+in vec4 vs_Col; // The array of vertex colors passed to the shader.
+
+out vec4 fs_Pos;
+out vec4 fs_Nor; // The array of normals that has been transformed by u_ModelInvTr. This is implicitly passed to the fragment shader.
+out vec4 fs_LightVec; // The direction in which our virtual light lies, relative to each vertex. This is implicitly passed to the fragment shader.
+out vec4 fs_Col; // The color of each vertex. This is implicitly passed to the fragment shader.
+
+const vec4 lightPos = vec4(5, 5, 5, 1); //The position of our virtual light, which is used to compute the shading of
+ //the geometry in the fragment shader.
+
+void main()
+{
+ fs_Col = vs_Col; // Pass the vertex colors to the fragment shader for interpolation
+
+ mat3 invTranspose = mat3(u_ModelInvTr);
+ fs_Nor = vec4(invTranspose * vec3(vs_Nor), 0); // Pass the vertex normals to the fragment shader for interpolation.
+ // Transform the geometry's normals by the inverse transpose of the
+ // model matrix. This is necessary to ensure the normals remain
+ // perpendicular to the surface after the surface is transformed by
+ // the model matrix.
+
+
+ vec4 modelposition = u_Model * vs_Pos; // Temporarily store the transformed vertex positions for use below
+ fs_Pos = modelposition;
+
+ modelposition.x += pow(sin((modelposition.y * 20.f + float(u_Time) * 0.05)), 2.0);
+ modelposition.y += sin((modelposition.y * 10.f + float(u_Time) * 0.05));
+
+ fs_LightVec = lightPos - modelposition; // Compute the direction in which the light source lies
+
+ gl_Position = u_ViewProj * modelposition;// gl_Position is a built-in variable of OpenGL which is
+ // used to render the final positions of the geometry's vertices
+}
diff --git a/src/shaders/planet-frag.glsl b/src/shaders/planet-frag.glsl
new file mode 100644
index 0000000..544c4e8
--- /dev/null
+++ b/src/shaders/planet-frag.glsl
@@ -0,0 +1,178 @@
+#version 300 es
+
+// This is a fragment shader. If you've opened this file first, please
+// open and read lambert.vert.glsl before reading on.
+// Unlike the vertex shader, the fragment shader actually does compute
+// the shading of geometry. For every pixel in your program's output
+// screen, the fragment shader is run for every bit of geometry that
+// particular pixel overlaps. By implicitly interpolating the position
+// data passed into the fragment shader by the vertex shader, the fragment shader
+// can compute what color to apply to its pixel based on things like vertex
+// position, light position, and vertex color.
+precision highp float;
+
+uniform highp int u_Time;
+uniform vec4 u_Color; // The color with which to render this instance of geometry.
+uniform vec4 u_CameraPos;
+
+// These are the interpolated values out of the rasterizer, so you can't know
+// their specific values without knowing the vertices that contributed to them
+in vec4 fs_Pos;
+in vec4 fs_Nor;
+in vec4 fs_LightVec;
+in vec4 fs_Col;
+in float noise;
+in float terrain_Type;
+in vec4 fs_LightPos;
+
+out vec4 out_Col; // This is the final output color that you will see on your
+ // screen for the pixel that is currently being processed.
+
+float random1( vec3 p ) {
+ return fract(sin((dot(p, vec3(127.1,
+ 311.7,
+ 191.999)))) *
+ 18.5453);
+}
+
+// Returns random vec3 in range [0, 1]
+vec3 random3(vec3 p) {
+ return fract(sin(vec3(dot(p,vec3(127.1, 311.7, 191.999)),
+ dot(p,vec3(269.5, 183.3, 765.54)),
+ dot(p, vec3(420.69, 631.2,109.21))))
+ *43758.5453);
+}
+
+float worley(vec3 p) {
+ vec3 pInt = floor(p);
+ vec3 pFract = fract(p);
+ float minDist = 1.0;
+ for (int x = -1; x <= 1; x++) {
+ for (int y = -1; y <= 1; y++) {
+ for (int z = -1; z <= 1; z++) {
+ vec3 neighbor = vec3(float(x), float(y), float(z));
+ vec3 voronoi = random3(pInt + neighbor);
+ //voronoi = 0.5 + 0.5 * sin(0.1 * float(u_Time) + 13.2831 * voronoi);
+ vec3 diff = neighbor + voronoi - pFract;
+ float dist = length(diff);
+ minDist = min(minDist, dist);
+ }
+ }
+ }
+ return 1.0 - minDist;
+}
+
+float smootherStep(float a, float b, float t) {
+ t = t*t*t*(t*(t*6.0 - 15.0) + 10.0);
+ return mix(a, b, t);
+}
+
+float interpNoise3D(float x, float y, float z) {
+ x *= 2.;
+ y *= 2.;
+ z *= 2.;
+ float intX = floor(x);
+ float fractX = fract(x);
+ float intY = floor(y);
+ float fractY = fract(y);
+ float intZ = floor(z);
+ float fractZ = fract(z);
+ float v1 = random1(vec3(intX, intY, intZ));
+ float v2 = random1(vec3(intX + 1., intY, intZ));
+ float v3 = random1(vec3(intX, intY + 1., intZ));
+ float v4 = random1(vec3(intX + 1., intY + 1., intZ));
+
+ float v5 = random1(vec3(intX, intY, intZ + 1.));
+ float v6 = random1(vec3(intX + 1., intY, intZ + 1.));
+ float v7 = random1(vec3(intX, intY + 1., intZ + 1.));
+ float v8 = random1(vec3(intX + 1., intY + 1., intZ + 1.));
+
+ float i1 = smootherStep(v1, v2, fractX);
+ float i2 = smootherStep(v3, v4, fractX);
+ float result1 = smootherStep(i1, i2, fractY);
+ float i3 = smootherStep(v5, v6, fractX);
+ float i4 = smootherStep(v7, v8, fractX);
+ float result2 = smootherStep(i3, i4, fractY);
+ return smootherStep(result1, result2, fractZ);
+}
+
+float fbm(float x, float y, float z, float octaves) {
+ float total = 0.;
+ float persistence = 0.5f;
+ for(float i = 1.; i <= octaves; i++) {
+ float freq = pow(2., i);
+ float amp = pow(persistence, i);
+ total += interpNoise3D(x * freq, y * freq, z * freq) * amp;
+ }
+ return total;
+}
+
+void main()
+{
+ vec4 view = normalize(u_CameraPos - fs_Pos);
+ vec4 H = normalize(view + normalize(fs_LightVec));
+ vec3 specularIntensity = pow(max(dot(H, normalize(fs_Nor)), 0.), 50.) * vec3(230./255., 233./255., 190./255.);
+
+ // Material base color (before shading)
+ vec4 diffuseColor = u_Color;
+
+ // Calculate the diffuse term for Lambert shading
+ float diffuseTerm = dot(normalize(fs_Nor), normalize(fs_LightVec));
+ // Avoid negative lighting values
+ diffuseTerm = clamp(diffuseTerm, 0.f, 1.f);
+
+ float ambientTerm = 0.3;
+
+ float lightIntensity = diffuseTerm + ambientTerm; //Add a small float value to the color multiplier
+ //to simulate ambient lighting. This ensures that faces that are not
+ //lit by our point light are not completely black.
+ vec3 color;
+ // Compute final shaded color
+ if (terrain_Type < 0.5) { // ocean color
+ float f = fbm(fs_Pos.x, fs_Pos.y, fs_Pos.z, 6.);
+ vec4 pos = fs_Pos;
+ pos = fs_Pos + f;
+ f = fbm(pos.x + .008*float(u_Time), pos.y, pos.z, 6.);
+ vec3 a = vec3(0.040, 0.50, 0.60);
+ vec3 b = vec3(0.00 ,0.4, 0.3);
+ vec3 c = vec3(0.00 , .8, .8);
+ vec3 d = vec3(0.050 ,0.1, 0.08);
+ color = a + b * cos(6.28 * (f * c + d));
+ specularIntensity = vec3(0.);
+ } else if (terrain_Type < 1.5) { // mountains
+ float f = fbm(fs_Pos.x * 2., fs_Pos.y * 2., fs_Pos.z * 2., 16.);
+ vec3 a = vec3(0.68, .66, .6);
+ vec3 b = vec3(0.250);
+ vec3 c = vec3(1.000);
+ vec3 d = vec3(0);
+ color = a + b * cos(6.28 * (worley(vec3(f)) * c + d));
+ } else if (terrain_Type < 2.5) { // terrace
+ float f = fbm(fs_Pos.x*1.5, fs_Pos.y*1.5, fs_Pos.z*1.5, 16.);
+ vec3 a = vec3(0.40, 0.7, 0.000);
+ vec3 b = vec3(.25);
+ vec3 c = vec3(.9);
+ vec3 d = vec3(0);
+ color = a + b * cos(6.28 * (f * c + d));
+ specularIntensity = vec3(0.);
+ } else if (terrain_Type <= 3.5) { // sand
+ float f = fbm(fs_Pos.x*2.5, fs_Pos.y*2.5, fs_Pos.z*2.5, 8.);
+ vec3 a = vec3(.9, .8, .7);
+ vec3 b = vec3(0.20);
+ vec3 c = vec3(1.000);
+ vec3 d = vec3(0);
+ color = a + b * cos(6.28 * (f * c + d));
+ } else {
+ color = vec3(0);
+ }
+
+ out_Col = vec4(color * lightIntensity + specularIntensity, 1.);
+ // out_Col = vec4(color, 1.);
+
+ vec3 height = vec3(noise);
+ height = (height + vec3(1.)) / 2.;
+ // out_Col = vec4(height, diffuseColor.a);
+ //out_Col = vec4(abs(fs_Nor.rgb), 1);
+ // out_Col = vec4(diffuseColor.rgb * lightIntensity, diffuseColor.a);
+
+ // out_Col = vec4((fs_Nor.xyz + vec3(1.)) * 0.5, 1.);
+}
diff --git a/src/shaders/planet-vert.glsl b/src/shaders/planet-vert.glsl
new file mode 100644
index 0000000..e6a3dae
--- /dev/null
+++ b/src/shaders/planet-vert.glsl
@@ -0,0 +1,347 @@
+#version 300 es
+
+//This is a vertex shader. While it is called a "shader" due to outdated conventions, this file
+//is used to apply matrix transformations to the arrays of vertex data passed to it.
+//Since this code is run on your GPU, each vertex is transformed simultaneously.
+//If it were run on your CPU, each vertex would have to be processed in a FOR loop, one at a time.
+//This simultaneous transformation allows your program to run much faster, especially when rendering
+//geometry with millions of vertices.
+
+uniform mat4 u_Model; // The matrix that defines the transformation of the
+ // object we're rendering. In this assignment,
+ // this will be the result of traversing your scene graph.
+
+uniform mat4 u_ModelInvTr; // The inverse transpose of the model matrix.
+ // This allows us to transform the object's normals properly
+ // if the object has been non-uniformly scaled.
+
+uniform mat4 u_ViewProj; // The matrix that defines the camera's transformation.
+ // We've written a static matrix for you to use for HW2,
+ // but in HW3 you'll have to generate one yourself
+uniform int u_Time;
+uniform vec4 u_CameraPos;
+uniform float u_Sea;
+uniform float u_Mountains;
+uniform float u_Fragments;
+uniform float u_PlanetAndMoon;
+
+in vec4 vs_Pos; // The array of vertex positions passed to the shader
+
+in vec4 vs_Nor; // The array of vertex normals passed to the shader
+
+in vec4 vs_Col; // The array of vertex colors passed to the shader.
+
+out float noise;
+out vec4 fs_Pos;
+out vec4 fs_Nor; // The array of normals that has been transformed by u_ModelInvTr. This is implicitly passed to the fragment shader.
+out vec4 fs_LightVec; // The direction in which our virtual light lies, relative to each vertex. This is implicitly passed to the fragment shader.
+out vec4 fs_Col; // The color of each vertex. This is implicitly passed to the fragment shader.
+out float terrain_Type;
+out vec4 fs_LightPos;
+
+float random1( vec3 p ) {
+ return fract(sin((dot(p, vec3(127.1,
+ 311.7,
+ 191.999)))) *
+ 18.5453);
+}
+
+// Returns random vec3 in range [0, 1]
+vec3 random3(vec3 p) {
+ return fract(sin(vec3(dot(p,vec3(127.1, 311.7, 191.999)),
+ dot(p,vec3(269.5, 183.3, 765.54)),
+ dot(p, vec3(420.69, 631.2,109.21))))
+ *43758.5453);
+}
+
+// Returns a surflet
+float surflet(vec3 p, vec3 corner) {
+ vec3 t = abs(p - corner);
+ vec3 falloff = vec3(1.f) - 6.f * vec3(pow(t.x, 5.f),pow(t.y, 5.f), pow(t.z, 5.f))
+ + 15.f * vec3(pow(t.x, 4.f), pow(t.y, 4.f),pow(t.z, 4.f))
+ - 10.f * vec3(pow(t.x, 3.f), pow(t.y, 3.f),pow(t.z, 3.f));
+ falloff = vec3(1.0) - 3.f * vec3(pow(t.x, 2.f),pow(t.y, 2.f), pow(t.z, 2.f))
+ + 2.f * vec3(pow(t.x, 3.f), pow(t.y, 3.f),pow(t.z, 3.f));
+ falloff = vec3(1.0) - t;
+ //falloff = vec3(1.f) - gain(t, .5);
+ vec3 gradient = random3(corner);
+ vec3 dist = p - corner;
+ float dotProd = dot(dist, gradient);
+ return dotProd * falloff.x * falloff.y * falloff.z;
+}
+
+float perlin(vec3 p) {
+ p = p * 4.5;
+ float surfletSum = 0.f;
+ for (int dx = 0; dx <= 1; dx++) {
+ for (int dy = 0; dy <= 1; dy++) {
+ for (int dz = 0; dz <= 1; dz++) {
+ surfletSum += surflet(p, vec3(floor(p.x), floor(p.y), floor(p.z)) + vec3(dx, dy, dz));
+ }
+ }
+ }
+ // float sum = surfletSum / 4.;
+ // return (sum + 1. )/2.; // kinda creates cool earth like land masses
+ return surfletSum / 4.;
+}
+
+float perlinTerrace(vec4 p) {
+ p *= 1.5;
+ float noise = perlin(vec3(p)) + .5 * perlin(2.f * vec3(p)) + 0.25 * perlin(4.f * vec3(p));
+ float rounded = (round(noise * 30.f) / 30.f);
+ float terrace = (noise + sin(290.*noise + 3.)*.004) *.8;
+ return terrace + .005;
+}
+
+float perlinMountains(vec4 p, float factor) {
+ p *= 2.;
+ float noise = perlin(vec3(p)) + .5 * perlin(2.f * vec3(p)) + 0.25 * perlin(4.f * vec3(p));
+ //noise = noise / (1.f + .5 + .25); // this and next line for valleys
+ //noise = pow(noise, .2);
+ noise *= factor;
+ return noise + .02;
+}
+
+vec4 cartesian(float r, float theta, float phi) {
+ return vec4(r * sin(phi) * cos(theta),
+ r * sin(phi) * sin(theta),
+ r * cos(phi), 1.);
+}
+
+// output is vec3(radius, theta, phi)
+vec3 polar(vec4 p) {
+ float r = sqrt(p.x * p.x + p.y * p.y + p.z * p.z);
+ float theta = atan(p.y / p.x);
+ // float phi = atan(sqrt(p.x * p.x + p.y * p.y) / p.z);
+ float phi = acos(p.z / sqrt(p.x * p.x + p.y * p.y + p.z * p.z));
+ return vec3(r, theta, phi);
+}
+
+vec4 transformToWorld(vec4 nor) {
+ vec3 normal = normalize(vec3(vs_Nor));
+ vec3 tangent = normalize(cross(vec3(0.0, 1.0, 0.0), normal));
+ vec3 bitangent = normalize(cross(normal, tangent));
+ mat4 transform;
+ transform[0] = vec4(tangent, 0.0);
+ transform[1] = vec4(bitangent, 0.0);
+ transform[2] = vec4(normal, 0.0);
+ transform[3] = vec4(0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 1.0);
+ return vec4(normalize(vec3(transform * nor)), 0.0);
+ // return nor;
+}
+
+vec4 perlinTerraceNormal(vec4 p) {
+ vec3 polars = polar(p);
+ float offset = .0001;
+ vec4 xNeg = cartesian(polars.x, polars.y - offset, polars.z);
+ vec4 xPos = cartesian(polars.x, polars.y + offset, polars.z);
+ vec4 yNeg = cartesian(polars.x, polars.y, polars.z - offset);
+ vec4 yPos = cartesian(polars.x, polars.y, polars.z + offset);
+ float xNegNoise = perlinTerrace(xNeg);
+ float xPosNoise = perlinTerrace(xPos);
+ float yNegNoise = perlinTerrace(yNeg);
+ float yPosNoise = perlinTerrace(yPos);
+
+ float xDiff = (xPosNoise - xNegNoise) * 1000.;
+ float yDiff = (yPosNoise - yNegNoise) * 1000.;
+ p.z = sqrt(1. - xDiff * xDiff - yDiff * yDiff);
+ return vec4(vec3(xDiff, yDiff, p.z), 0);
+ // vec3 normal = vec3(vs_Nor);
+ // vec3 tangent = cross(vec3(0, 1, 0), normal);
+ // vec3 bitangent = cross(normal, tangent);
+ // vec3 p1 = vec3(vs_Pos) + .0001 * tangent + tangent * perlinTerrace(p + vec4(.0001*tangent, 0.));
+ // vec3 p2 = vec3(vs_Pos) + .0001 * bitangent + bitangent * perlinTerrace(p + vec4(.0001*bitangent, 0.));
+ // vec3 p3 = vec3(vs_Pos) + normal * perlinTerrace(p);
+ // return vec4(cross(p3 - p1, p3 - p2), 0);
+}
+
+vec4 perlinMoutainNormal(vec4 p, float factor) {
+ vec3 polars = polar(p);
+ float offset = .01;
+ vec4 xNeg = cartesian(polars.x, polars.y - offset, polars.z);
+ vec4 xPos = cartesian(polars.x, polars.y + offset, polars.z);
+ vec4 yNeg = cartesian(polars.x, polars.y, polars.z - offset);
+ vec4 yPos = cartesian(polars.x, polars.y, polars.z + offset);
+ float xNegNoise = perlinMountains(xNeg, factor);
+ float xPosNoise = perlinMountains(xPos, factor);
+ float yNegNoise = perlinMountains(yNeg, factor);
+ float yPosNoise = perlinMountains(yPos, factor);
+
+ float xDiff = (xPosNoise - xNegNoise) * 10.;
+ float yDiff = (yPosNoise - yNegNoise) * 10.;
+ p.z = sqrt(1. - xDiff * xDiff - yDiff * yDiff);
+ return vec4(vec3(xDiff, yDiff, p.z), 0);
+}
+
+
+float fbmRandom( vec3 p ) {
+ return fract(sin((dot(p, vec3(127.1,
+ 311.7,
+ 191.999)))) *
+ 18.5453);
+}
+
+float smootherStep(float a, float b, float t) {
+ t = t*t*t*(t*(t*6.0 - 15.0) + 10.0);
+ return mix(a, b, t);
+}
+
+float interpNoise3D(float x, float y, float z) {
+ x *= 2.;
+ y *= 2.;
+ z *= 2.;
+ float intX = floor(x);
+ float fractX = fract(x);
+ float intY = floor(y);
+ float fractY = fract(y);
+ float intZ = floor(z);
+ float fractZ = fract(z);
+ float v1 = fbmRandom(vec3(intX, intY, intZ));
+ float v2 = fbmRandom(vec3(intX + 1., intY, intZ));
+ float v3 = fbmRandom(vec3(intX, intY + 1., intZ));
+ float v4 = fbmRandom(vec3(intX + 1., intY + 1., intZ));
+
+ float v5 = fbmRandom(vec3(intX, intY, intZ + 1.));
+ float v6 = fbmRandom(vec3(intX + 1., intY, intZ + 1.));
+ float v7 = fbmRandom(vec3(intX, intY + 1., intZ + 1.));
+ float v8 = fbmRandom(vec3(intX + 1., intY + 1., intZ + 1.));
+
+ float i1 = smootherStep(v1, v2, fractX);
+ float i2 = smootherStep(v3, v4, fractX);
+ float result1 = smootherStep(i1, i2, fractY);
+ float i3 = smootherStep(v5, v6, fractX);
+ float i4 = smootherStep(v7, v8, fractX);
+ float result2 = smootherStep(i3, i4, fractY);
+ return smootherStep(result1, result2, fractZ);
+}
+
+float fbm(vec4 p, float oct, float freq) {
+ float total = 0.;
+ float persistence = 0.5f;
+ float octaves = oct;
+ for(float i = 1.; i <= octaves; i++) {
+ float freq = pow(freq, i);
+ float amp = pow(persistence, i);
+ total += interpNoise3D(p.x * freq, p.y * freq, p.z * freq) * amp;
+ }
+ return total;
+}
+
+float fbm2(vec4 p) {
+ float total = 0.;
+ float persistence = 0.5f;
+ float octaves = 4.;
+ for(float i = 1.; i <= octaves; i++) {
+ float freq = pow(2.f, i);
+ float amp = pow(persistence, i);
+ total += interpNoise3D(p.x * freq, p.y * freq, p.z * freq) * amp;
+ }
+ return total;
+}
+
+vec4 fbmNormal(vec4 p, float oct, float freq) {
+ float xNeg = fbm((p + vec4(-.00001, 0, 0, 0)), oct, freq);
+ float xPos = fbm((p + vec4(.00001, 0, 0, 0)), oct, freq);
+ float xDiff = xPos - xNeg;
+ float yNeg = fbm((p + vec4(0, -.00001, 0, 0)), oct, freq);
+ float yPos = fbm((p + vec4(0, .00001, 0, 0)), oct, freq);
+ float yDiff = yPos - yNeg;
+ float zNeg = fbm((p + vec4(0, 0, -.00001, 0)), oct, freq);
+ float zPos = fbm((p + vec4(0, 0, .00001, 0)), oct, freq);
+ float zDiff = zPos - zNeg;
+ return vec4(vec3(xDiff, yDiff, zDiff), 0);
+}
+
+float worley(vec3 p) {
+ vec3 pInt = floor(p);
+ vec3 pFract = fract(p);
+ float minDist = 1.0;
+ for (int x = -1; x <= 1; x++) {
+ for (int y = -1; y <= 1; y++) {
+ for (int z = -1; z <= 1; z++) {
+ vec3 neighbor = vec3(float(x), float(y), float(z));
+ vec3 voronoi = random3(pInt + neighbor);
+ vec3 diff = neighbor + voronoi - pFract;
+ float dist = length(diff);
+ minDist = min(minDist, dist);
+ }
+ }
+ }
+ return 1.0 - minDist;
+}
+
+vec4 getTerrain() {
+ // biomes = water, terraces, mountains, sand
+ // toolbox = smooth step (fbm and perlin), sin wave (terraces), jitter scattering (worley), gain to animate light
+ // gui = modify boundaries of terrains, modify fbm octaves or freq,
+ float terrainMap = worley(vec3(fbm(vs_Pos, 6., 1.2 + u_Fragments * .1)));
+ vec4 noisePos = vs_Pos;
+ if (terrainMap < .28 + (u_Sea * .06)) {
+ // water (use worley to animate?) and use blinn phong?
+ fs_Nor = vs_Nor;
+ terrain_Type = 0.;
+ } else if (terrainMap < .3) {
+ fs_Nor = vs_Nor;
+ terrain_Type = 3.;
+ } else if (terrainMap < .94 - (u_Mountains * .05)) {
+ // terraces
+ noisePos = vs_Pos + vs_Nor * perlinTerrace(vs_Pos);
+ fs_Nor = transformToWorld(normalize(perlinTerraceNormal(vs_Pos)));
+ terrain_Type = 2.;
+ } else if (terrainMap < .98 - (u_Mountains * .05)) {
+ // smaller mountains
+ noisePos = vs_Pos + vs_Nor * perlinMountains(vs_Pos, 1.);
+ fs_Nor = transformToWorld(normalize(perlinMoutainNormal(vs_Pos, .4)));
+ terrain_Type = 1.;
+ } else {
+ // mountains
+ noisePos = vs_Pos + vs_Nor * perlinMountains(vs_Pos, 1.7);
+ fs_Nor = transformToWorld(normalize(perlinMoutainNormal(vs_Pos, 1.7)));
+ terrain_Type = 1.;
+ }
+ return noisePos;
+}
+
+float GetBias(float time, float bias)
+{
+ return (time / ((((1.0/bias) - 2.0)*(1.0 - time))+1.0));
+}
+
+float GetGain(float time, float gain)
+{
+ if(time < 0.5)
+ return GetBias(time * 2.0,gain)/2.0;
+ else
+ return GetBias(time * 2.0 - 1.0,1.0 - gain)/2.0 + 0.5;
+}
+
+void main()
+{
+ fs_Col = vs_Col;
+ mat3 invTranspose = mat3(u_ModelInvTr);
+ fs_Nor = vec4(invTranspose * vec3(vs_Nor), 0);
+
+ vec4 noisePos = getTerrain();
+
+ vec4 modelposition = u_Model * noisePos;
+ fs_Pos = modelposition;
+
+ fs_Nor = vec4(invTranspose * vec3(fs_Nor), 0);
+
+ vec4 light;
+ if (u_PlanetAndMoon > 0.) {
+ float angle = .01 * float(u_Time);
+ vec4 col0 = vec4(cos(angle), 0, -1.*sin(angle), 0);
+ vec4 col1 = vec4(0, 1, 0, 0);
+ vec4 col2 = vec4(sin(angle), 0, cos(angle), 0);
+ vec4 col3 = vec4(0, 0, 0, 1);
+ mat4 rotate = mat4(col0, col1, col2, col3);
+ light = rotate * vec4(-2, 0, 0, 1);
+ } else {
+ light = mix(vec4(10., 4., 10., 1.), vec4(-10., 4., 10., 1.), GetGain((sin(float(u_Time)*.02) + 1.)/2., .75));
+ }
+ fs_LightPos = light;
+ fs_LightVec = light - modelposition; // Compute the direction in which the light source lies
+ gl_Position = u_ViewProj * modelposition;// gl_Position is a built-in variable of OpenGL which is
+ // used to render the final positions of the geometry's vertices
+}
diff --git a/src/shaders/test-frag.glsl b/src/shaders/test-frag.glsl
new file mode 100644
index 0000000..8ad9123
--- /dev/null
+++ b/src/shaders/test-frag.glsl
@@ -0,0 +1,182 @@
+#version 300 es
+
+precision highp float;
+
+uniform vec4 u_Color;
+uniform highp int u_Time;
+
+in vec4 fs_Pos;
+in vec4 fs_Nor;
+in vec4 fs_LightVec;
+in vec4 fs_Col;
+
+out vec4 out_Col;
+
+// Returns random vec3 in range [0, 1]
+vec3 random3(vec3 p) {
+ return fract(sin(vec3(dot(p,vec3(127.1, 311.7, 191.999)),
+ dot(p,vec3(269.5, 183.3, 765.54)),
+ dot(p, vec3(420.69, 631.2,109.21))))
+ *43758.5453);
+}
+
+// Returns a surflet
+float surflet(vec3 p, vec3 corner) {
+ vec3 t = abs(p - corner);
+ vec3 falloff = vec3(1.f) - 6.f * vec3(pow(t.x, 5.f),pow(t.y, 5.f), pow(t.z, 5.f))
+ + 15.f * vec3(pow(t.x, 4.f), pow(t.y, 4.f),pow(t.z, 4.f))
+ - 10.f * vec3(pow(t.x, 3.f), pow(t.y, 3.f),pow(t.z, 3.f));
+ vec3 gradient = random3(corner);
+ vec3 dist = p - corner;
+ float dotProd = dot(dist, gradient);
+ return dotProd * falloff.x * falloff.y * falloff.z;
+}
+
+float perlin(vec3 p) {
+ p = p * 2.5;
+ float surfletSum = 0.f;
+ for (int dx = 0; dx <= 1; dx++) {
+ for (int dy = 0; dy <= 1; dy++) {
+ for (int dz = 0; dz <= 1; dz++) {
+ surfletSum += surflet(p, vec3(floor(p.x), floor(p.y), floor(p.z)) + vec3(dx, dy, dz));
+ }
+ }
+ }
+ return surfletSum;
+}
+
+float worley(vec3 p) {
+ vec3 pInt = floor(p);
+ vec3 pFract = fract(p);
+ float minDist = 1.0;
+ float secondDist = 1.0;
+ for (int x = -1; x <= 1; x++) {
+ for (int y = -1; y <= 1; y++) {
+ for (int z = -1; z <= 1; z++) {
+ vec3 neighbor = vec3(float(x), float(y), float(z));
+ vec3 voronoi = random3(pInt + neighbor);
+ //voronoi = 0.5 + 0.5 * sin(0.1 * float(u_Time) + 13.2831 * voronoi);
+ vec3 diff = neighbor + voronoi - pFract;
+ float dist = length(diff);
+ if (dist < minDist) {
+ secondDist = minDist;
+ minDist = dist;
+ } else if (dist < secondDist) {
+ secondDist = dist;
+ }
+ //minDist = min(minDist, dist);
+ }
+ }
+ }
+ return 1.0 - minDist;
+ //return -1. * minDist + 1. * secondDist;
+}
+
+float random1( vec3 p ) {
+ return fract(sin((dot(p, vec3(127.1,
+ 311.7,
+ 191.999)))) *
+ 18.5453);
+}
+
+float smootherStep(float a, float b, float t) {
+ t = t*t*t*(t*(t*6.0 - 15.0) + 10.0);
+ return mix(a, b, t);
+}
+
+float interpNoise3D(float x, float y, float z) {
+ x *= 2.;
+ y *= 2.;
+ z *= 2.;
+ float intX = floor(x);
+ float fractX = fract(x);
+ float intY = floor(y);
+ float fractY = fract(y);
+ float intZ = floor(z);
+ float fractZ = fract(z);
+ float v1 = random1(vec3(intX, intY, intZ));
+ float v2 = random1(vec3(intX + 1., intY, intZ));
+ float v3 = random1(vec3(intX, intY + 1., intZ));
+ float v4 = random1(vec3(intX + 1., intY + 1., intZ));
+
+ float v5 = random1(vec3(intX, intY, intZ + 1.));
+ float v6 = random1(vec3(intX + 1., intY, intZ + 1.));
+ float v7 = random1(vec3(intX, intY + 1., intZ + 1.));
+ float v8 = random1(vec3(intX + 1., intY + 1., intZ + 1.));
+
+ float i1 = smootherStep(v1, v2, fractX);
+ float i2 = smootherStep(v3, v4, fractX);
+ float result1 = smootherStep(i1, i2, fractY);
+ float i3 = smootherStep(v5, v6, fractX);
+ float i4 = smootherStep(v7, v8, fractX);
+ float result2 = smootherStep(i3, i4, fractY);
+ return smootherStep(result1, result2, fractZ);
+}
+
+float fbm(float x, float y, float z) {
+ float total = 0.;
+ float persistence = 0.5f;
+ float octaves = 6.;
+ for(float i = 1.; i <= octaves; i++) {
+ float freq = pow(2., i);
+ float amp = pow(persistence, i);
+ total += interpNoise3D(x * freq, y * freq, z * freq) * amp;
+ }
+ return total;
+}
+
+void main()
+{
+ // vec4 diffuseColor = u_Color;
+
+ // // Calculate the diffuse term for Lambert shading
+ // float diffuseTerm = dot(normalize(fs_Nor), normalize(fs_LightVec));
+ // // Avoid negative lighting values
+ // diffuseTerm = clamp(diffuseTerm, 0.f, 1.f);
+
+ // float ambientTerm = 0.4;
+
+ // float lightIntensity = diffuseTerm + ambientTerm; //Add a small float value to the color multiplier
+ // //to simulate ambient lighting. This ensures that faces that are not
+ // //lit by our point light are not completely black.
+ // float perlinNoise = perlin(vec3(fs_Pos));
+ // vec3 a = vec3(u_Color);
+ // vec3 b = vec3(0.688, 0.558, 0.500);
+ // vec3 c = vec3(255.0 / 255.0, 244.0 / 255.0, 224.0 / 255.0);
+ // vec3 d = vec3(0.588, -0.342, 0.048);
+ // vec3 perlinColor = a + b * cos(6.28 * worley(vec3(fs_Pos)) * perlinNoise * 4. * c + d);
+
+ // Compute final shaded color
+ float f = fbm(fs_Pos.x, fs_Pos.y, fs_Pos.z);
+ vec4 pos = fs_Pos;
+ pos = fs_Pos + f; // THIS IS COOL!!!!!!!!!!!!
+ // f = fbm(pos.x, pos.y + .001*float(u_Time), pos.z);
+
+ vec3 a = vec3(1, .9, .8);
+ vec3 b = vec3(0.20);
+ vec3 c = vec3(1.000);
+ vec3 d = vec3(0);
+ vec3 color = a + b * cos(6.28 * (f * c + d));
+
+ out_Col = vec4(color, 1.); // swirly fbm
+
+ // loat terrainMap = worley(vec3(f));
+ // if (terrainMap < .28) {
+ // color = vec3(.2, .2, .8);
+ // } else if (terrainMap < .3) {
+ // color = vec3(.5, .5, .2);
+ // } else if (terrainMap < .44) {
+ // color = vec3(.2, .8, .2);
+ // } else if (terrainMap < .48) {
+ // color = vec3(.5, .5, .5);
+ // } else {
+ // color = vec3(0);
+ // }f
+
+ // vec3 a = vec3(0.9);
+ // vec3 b = vec3(0.250);
+ // vec3 c = vec3(1.000);
+ // vec3 d = vec3(0);
+ // vec3 color = a + b * cos(6.28 * (worley(vec3(f)) * c + d));
+ out_Col = vec4(color, 1); //worley and fbm (lowered octave from 4 to 2 for bigger chunks)
+}
diff --git a/src/shaders/test-vert.glsl b/src/shaders/test-vert.glsl
new file mode 100644
index 0000000..ddf5a5f
--- /dev/null
+++ b/src/shaders/test-vert.glsl
@@ -0,0 +1,55 @@
+#version 300 es
+
+//This is a vertex shader. While it is called a "shader" due to outdated conventions, this file
+//is used to apply matrix transformations to the arrays of vertex data passed to it.
+//Since this code is run on your GPU, each vertex is transformed simultaneously.
+//If it were run on your CPU, each vertex would have to be processed in a FOR loop, one at a time.
+//This simultaneous transformation allows your program to run much faster, especially when rendering
+//geometry with millions of vertices.
+
+uniform mat4 u_Model; // The matrix that defines the transformation of the
+ // object we're rendering. In this assignment,
+ // this will be the result of traversing your scene graph.
+
+uniform mat4 u_ModelInvTr; // The inverse transpose of the model matrix.
+ // This allows us to transform the object's normals properly
+ // if the object has been non-uniformly scaled.
+
+uniform mat4 u_ViewProj; // The matrix that defines the camera's transformation.
+ // We've written a static matrix for you to use for HW2,
+ // but in HW3 you'll have to generate one yourself
+
+in vec4 vs_Pos; // The array of vertex positions passed to the shader
+
+in vec4 vs_Nor; // The array of vertex normals passed to the shader
+
+in vec4 vs_Col; // The array of vertex colors passed to the shader.
+
+out vec4 fs_Pos;
+out vec4 fs_Nor; // The array of normals that has been transformed by u_ModelInvTr. This is implicitly passed to the fragment shader.
+out vec4 fs_LightVec; // The direction in which our virtual light lies, relative to each vertex. This is implicitly passed to the fragment shader.
+out vec4 fs_Col; // The color of each vertex. This is implicitly passed to the fragment shader.
+
+const vec4 lightPos = vec4(5, 5, 3, 1); //The position of our virtual light, which is used to compute the shading of
+ //the geometry in the fragment shader.
+
+void main()
+{
+ fs_Col = vs_Col; // Pass the vertex colors to the fragment shader for interpolation
+
+ mat3 invTranspose = mat3(u_ModelInvTr);
+ fs_Nor = vec4(invTranspose * vec3(vs_Nor), 0); // Pass the vertex normals to the fragment shader for interpolation.
+ // Transform the geometry's normals by the inverse transpose of the
+ // model matrix. This is necessary to ensure the normals remain
+ // perpendicular to the surface after the surface is transformed by
+ // the model matrix.
+
+
+ vec4 modelposition = u_Model * vs_Pos; // Temporarily store the transformed vertex positions for use below
+ fs_Pos = modelposition;
+
+ fs_LightVec = lightPos - modelposition; // Compute the direction in which the light source lies
+
+ gl_Position = u_ViewProj * modelposition;// gl_Position is a built-in variable of OpenGL which is
+ // used to render the final positions of the geometry's vertices
+}
 -
- -
-