Replies: 7 comments 2 replies
-
|
so from the sample program, I say you start the whole thing from the "C#" side, with a new worker: but how do you start it from the "javascript" side, with plain js? |
Beta Was this translation helpful? Give feedback.
-
|
Hi @nextfool,
Perhaps we can clarify as follows: The "main js" level can be thought of as just another worker. Consider that workers can create their own workers, potentially yielding a tree-like hierarchy. The engine at each node requires the following additions to its bare JavaScript environment:
The only difference at the root node (the "main js" level) is that (3) isn't required, as there's no parent node. Because the other additions are common to all levels, we use Please let us know if you have additional questions or comments. Thanks! |
Beta Was this translation helpful? Give feedback.
-
|
Hi @nextfool,
Please see our updates in this repository. The worker scripts are now in separate JavaScript files, and the
Because each worker has its own instance of the JavaScript runtime, it can't share objects or functions directly with other workers. This sample does include Web Workers support transferable objects, but ClearScript has no such facility. It does allow you to pass script objects – including functions – from one script engine to another, but we don't recommend that. Access to such an object must always go through ClearScript, so there's significant overhead and potentially other issues.
The module block proposal calls for changes to the JavaScript language, so it's outside the scope of the ClearScript project. If and when V8 adopts module blocks, ClearScript will support them. Cheers! |
Beta Was this translation helpful? Give feedback.
-
|
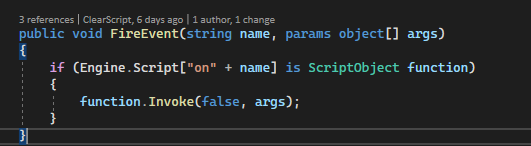
Hi @ClearScriptLib So I have another related question: To execute the event handler, you try to search for the handler name among the "global functions" But in the browser world, we usually have something like this: var worker1 = new Worker("worker1.js"); var worker2 = new Worker("worker2.js"); I can, of cause, just define a global message handler like this: But in this case, I would not be able to tell which worker actually sent the message. So my question is, how do you implement an event handler that is attached to one specific worker instance? |
Beta Was this translation helpful? Give feedback.
-
|
Hi @nextfool,
Please see our latest updates in this repository. The Thanks! |
Beta Was this translation helpful? Give feedback.
-
|
Hi @ClearScriptLib ,
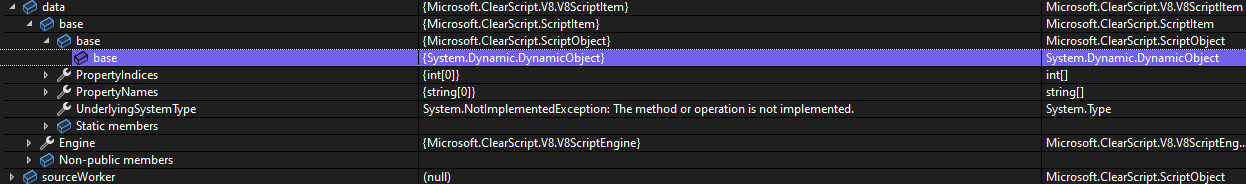
As you can see, if I just post the array buffer by reference, after it was "stringnified" by the "JSON" serializer, the "data" parameter is always an empty pair of curly brackets "{}", which means the js "JSON" serializer just can't serialize the "buff". I am not sure what this "buff" really is, maybe a pointer to memory address? If I just pass the data without serializing like above, with vs debugger, I could see a "V8ScriptItem" but I just can not get the inside detail of this item because it is from the V8 native code. Can you give me an idea of how to deal with the buffer reference from the V8 native code? Or do you have any different thoughts on the "SharedArrayBuffer" implementation? Thank you very much for your help. |
Beta Was this translation helpful? Give feedback.
-
|
Hi @nextfool, Please see our response here. Thank you! |
Beta Was this translation helpful? Give feedback.


Uh oh!
There was an error while loading. Please reload this page.
-
Hi @ClearScriptLib ,
Sorry its a tricky question, I am trying to make my self clear:
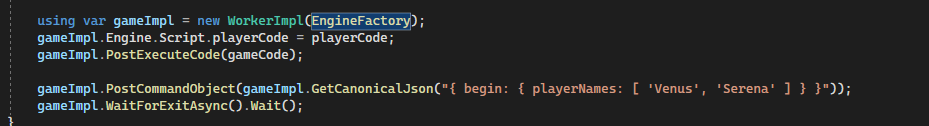
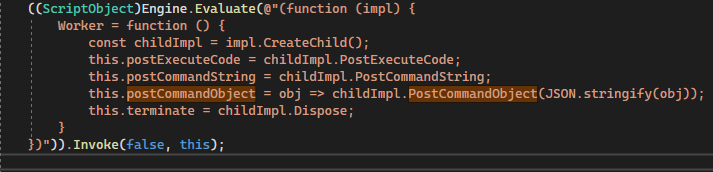
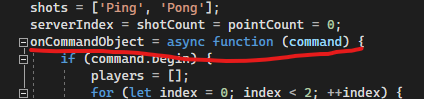
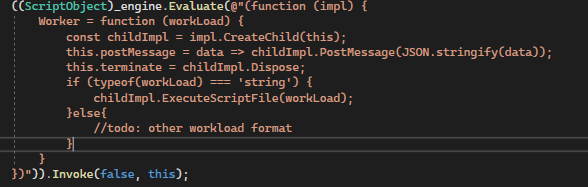
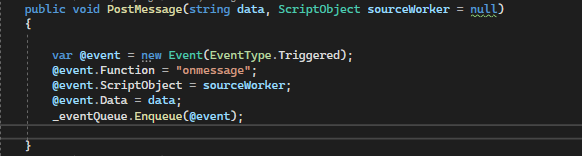
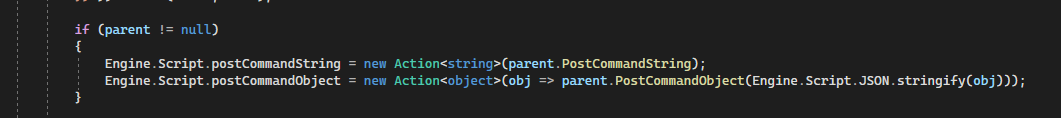
So I have checked the code in "WorkerImpl", what I've learned here is that:
from my understanding, the above is the key part to implement the communication between a parent work and a child worker (in this case, there at least 3 "levels" of the js code involved, app's main js--> parent worker --> child worker, so the above implementation is all about communication between level 2 and level 3),
but, what if I only need communication between level 1 and level 2? I mean between app's main js and first level worker, lets say we have something like this in a app's main.js which is just a plain js file(no workers involved):
var myWorker = new Worker("my-worker-source.js")
myWorker .postXXX(data);
myWorker .onmessage(function(){
//revieved message from myWorker
});
so in "my-worker-source.js", to send data to the "plain main js", we may need something like:
postXXX(data);
So my question is: how do I implement this "PostXXX" methods for the "plain main js", do I need to put a postXXX to the global Engine.Script? how about the message queue, do I also need to include it in my "root“ engine? do I also need the message loop logic in the root engine?
Thank you.
Beta Was this translation helpful? Give feedback.
All reactions