Documentation about common queries against the prescribing dataset.
You will need a Google account with the correct permissions (set up by an administrator) to access our BigQuery account.
Then follow this quickstart (ignoring the first section "Before you begin")
BigQuery provides a SQL-like interface to massive datasets. It has two dialects, "Legacy" and "standard". When running a query, the default is "Legacy"; you must select "standard" in the options section to use that. Nearly all the examples here are in "standard" format, which is compatible with standard SQL. However, sometimes it is necessary to use "Legacy" format as some functions have not yet been ported by Google to the newer format.
Standard SQL supports temp tables which can make your queries more readable than using lots of subqueries.
Legacy SQL used to have a more extensive range of aggregate functions, and in particular, window functions. However, OpenPrescribing is now able to use standard SQL exclusively.
A comparison between the two formats is here.
BigQuery is billed by the amount of data queried. Querying the entire prescribing table costs about 20 cents. You should bear these costs in mind if running large numbers of queries. Good practice is to extract, say, one month of data to a new table to design your queries, e.g. running
SELECT *
FROM ebmdatalab.hscic.prescribing
WHERE month = TIMESTAMP('2016-06-01')...and selecting "save to table". If you then save this to a table ebmdatalb.tmp.<something>, then you can continue to design your query like:
SELECT *
FROM ebmdatalab.tmp.<something>
WHERE bnf_code LIKE '02%'
LIMIT 1000-
hscic.prescribing- The main prescribing dataset.
- Updated monthly. Data going back to Aug 2010.
- Data from https://apps.nhsbsa.nhs.uk/infosystems/data/showDataSelector.do?reportId=124
- You probably want to query one of the
normalised_prescribing_*tables, described below - Contains one row per practice per presentation per month
- Fields:
sha: Area team code (TODO: what is this?)pct: Identifier of CCGpractice: Identifier of practicebnf_code: BNF code of presentationbnf_name: Name of presentation in BNFitems: Number of items, where "item" means "appearance on a prescription"net_cost: The cost of the presentation that month to that practice, according to the Drug Tariffactual_cost: The actual cost when taking into account adjustments for bulk purchases, out of pocket expenses, etc. This is the "cost" field that we usually want to queryquantity: number of pills/grams/millilitres/dressings/ampoules prescribedmonth: Month, as aTIMESTAMPof the first millisecond of the month
-
hscic.normalised_prescribing_standardandhscic.normalised_prescribing_legacy- Views on the
prescribingtable that normalise thepctandbnf_codefields as described below. - In most cases, this is the table you will want to query.
- The data is the same in both tables. Use
normalised_prescribing_standardwhen you want to use Standard SQL, andnormalised_prescribing_legacywhen you want to use Legacy SQL. - Fields
- As for the
prescribingtable, except:- The
pctfield is renamed toccg_id, and is the identifier of the CCG that the practice is currently in, as it may have moved between CCGs - The
bnf_codefield is the most recent version of the BNF code
- The
- As for the
- Views on the
-
hscic.practices:- All the practices in England.
- Updated quarterly.
- Data from https://digital.nhs.uk/services/organisation-data-service/data-downloads/gp-and-gp-practice-related-data
- Practices with a
settingof4are standard GP practices (see below for a full list ofsettingss) - Fields:
code: Identifier of practicename: Name of practiceaddress1toaddress5,postcode: Portions of addresslocation: Location of practice in WG84 formatccg_id: Identifier of practice's current CCGsetting: See below for a full list ofsettingssclose_date: Date practice closedjoin_provider_date: Date practice joined CCGleave_provider_date: Date practice closedopen_date: Data practice openedstatus_code: One of the following: *A: Active *B: Retired *C: Closed *D: Dormant *P: Proposed *U: Unknown
-
hscic.ccgs:- All the CCGs in England.
- Updated quarterly.
- Data from https://digital.nhs.uk/services/organisation-data-service/data-downloads/other-nhs-organisations
- Fields:
code: Identifier of CCGname: Name of CCGons_code: ONS codeorg_type: One of the following:CCGPCTUnknown
open_date: Date CCG was formedclose_date: Date CCG closedaddress,postcode: Address of principal office
-
hscic.practice_statistics:- Total list size, STAR-PU, ASTRO-PU, and list sizes stratified by gender and age group for each practice.
- Updated monthly.
- Data from https://digital.nhs.uk/data-and-information/publications/statistical/patients-registered-at-a-gp-practice
- Fields:
monthpracticepct_idtotal_list_sizeastro_pu_costastro_pu_itemsstar_pu- For each age group in :
0_4,15_24,25_34,35_44,45_54,55_64,5_14,65_74,75_plusfemale_{age_group}male_{age_group}
-
hscic.presentation:- BNF code, name, ADQs for each presentation.
- BNF data:
- Updated monthly
- Data from https://apps.nhsbsa.nhs.uk/infosystems/data/showDataSelector.do?reportId=126
- ADQs updated manually when new data available.
- Fields:
bnf_codenameis_genericactive_quantityadqadq_unitpercent_of_adq
-
hscic.ppu_savings:- Price per Unit savings
- Updated monthly based on prescribing data
- Fields:
datepct_idpractice_idbnf_codelowest_decilequantityprice_per_unitpossible_savingsformulation_swap
-
dmd.product:- Products (both AMPs and VMPS) in dm+d
- Updated monthly
- Data from https://isd.digital.nhs.uk/trud3/user/authenticated/group/0/pack/6/subpack/24/releases
- See https://www.nhsbsa.nhs.uk/sites/default/files/2017-02/dmd_Implemention_Guide_%28Primary_Care%29_v1.0.pdf for details of fields
-
dmd.tariffprice:- Monthly prices according to the Drug Tariff
- Updated monthly
- Data from https://www.nhsbsa.nhs.uk/pharmacies-gp-practices-and-appliance-contractors/drug-tariff/drug-tariff-part-viii/
- Fields:
datevmppproducttariff_categoryprice_pence
-
dmd.ncsoconcession:- Temporary alterations to official Drug Tariff prices in response to things like shortages, etc
- Updated monthly, or when new data is available
- Data from http://psnc.org.uk/dispensing-supply/supply-chain/generic-shortages/ncso-archive/
- Fields:
vmppdatedrugpack_sizeprice_concession_pence
-
dmd.vmpp- Virtual Medicinal Product Packs (part of the dm+d data model, see our dm+d notes for more details)
- Used for linking tariffs and concessions to products
- Fields:
vvpid: Primary key, corresponds totariffprice.vmppandncsoconcession.vmppinvalidnmabbrevnmvpidqtyvalqty_uomcdcombpackcd
The different kinds of practice available in the setting column of the practices table are as follows:
- 0 = Other
- 1 = WIC Practice
- 2 = OOH Practice
- 3 = WIC + OOH Practice
- 4 = GP Practice
- 8 = Public Health Service
- 9 = Community Health Service
- 10 = Hospital Service
- 11 = Optometry Service
- 12 = Urgent & Emergency Care
- 13 = Hospice
- 14 = Care Home / Nursing Home
- 15 = Border Force
- 16 = Young Offender Institution
- 17 = Secure Training Centre
- 18 = Secure Children's Home
- 19 = Immigration Removal Centre
- 20 = Court
- 21 = Police Custody
- 22 = Sexual Assault Referral Centre (SARC)
- 24 = Other
The datain the prescribing table covers prescriptions prescribed by GPs and other non-medical prescribers (nurses, pharmacists and others) in England and dispensed in the community in the UK. Prescriptions written in England but dispensed outside England are included.
The format of the data in the prescribing table is documented by the NHS here.
The unique identifier for the item prescribed is the bnf_code.
The BNF (British National Formulary) is the de facto standard list of medicines used UK prescribing. Maintained by the British Medical Association and the Royal Pharmaceutical Society, it lists indications, dosages, side effects and so on for more than 70,000 medicines.
The prescribing data uses a modified version of the BNF which was current in 2014, with custom additions and alterations. The resulting system is called a BNF pseudo-classification and is described here. In particular, appliances are not listed in the BNF at all, so are included in the pseudo-classification with sections named DUMMY SECTION.
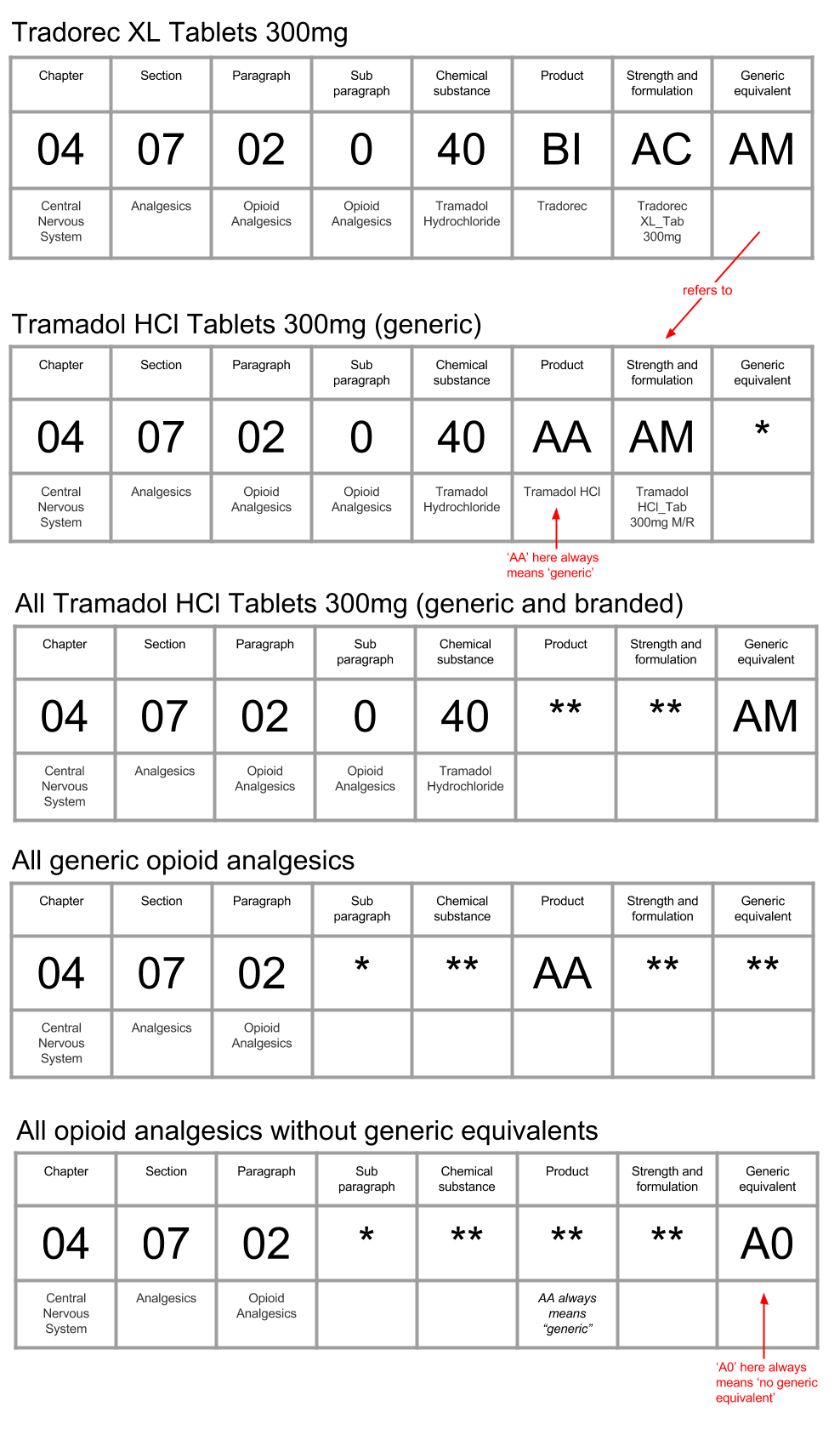
The first characters of the code provide a hierarchical classification of the presentation.
The last few characters identify individual presentations, and a way of identifying their generic equivalents.
The image below shows how you might examine Tramadol. Tramadol is an opiod pain medicine, available in the UK as tablets (i.e. pills), capsules (i.e. gelatine things), patches, liquids and more. Just focussing on tablets, these are available as standard tablets, and modified release tablets (which are absorbed by the body over a longer period of time, allowing the patient to take less frequent doses). Modified release tablets are available in 50mg, 100mg, 150mg, 200mg, 300mg and 400mg pills.