Credit Card Transactions:

A capstone project for Data Scientist Bootcamp Certification.
Building the Machine Learning Model.
A credit card is one of the most used financial products to make online purchases and payments, which should be safe from fraud. Hence, is important that credit card companies recognize fraudulent credit card transactions so that customers are not charged for items they did not purchase.
To build a Machine Learning classification model with a Classifier to predict whether a creditcard transaction is fraudulent or not. The project aims at testing the personal skills in Machine Learning Model building aiming at building a classifier with a predictive power with accuracy above 75%.
Python language is used throughout the project.
- Data Collection.
- Exploratory Data Analysis: Analyze and understand the data to identify patterns, relationships, and trends in the data by using Descriptive Statistics and Visualizations.
- Data Cleaning: This might include standardization, handling the missing values and outliers in the data.
- Dealing with Imbalanced data: This data set is highly imbalanced. The data should be balanced using the appropriate methods before moving onto model building.
- Feature Engineering: Create new features or transform the existing features for better performance of the ML Models.
- Model Selection: Choose the most appropriate model that can be used for this project.
- Model Training: Split the data into train & test sets and use the train set to estimate the best model parameters.
- Model Validation: Evaluate the performance of the model on data that was not used during the training process. The goal is to estimate the model's ability to generalize to new, unseen data and to identify any issues with the model, such as overfitting.
- Model Deployment: Model deployment is the process of making a trained machine learning model available for use in a production environment.
Creditcard records collected for the two-day transactions in Europe whereby the dataset is provided by KnowledgeHud upGrad as one of the choices among many project concepts learners to consider.
The dataset contains transactions made by credit cards in September 2013 by European cardholders. This dataset presents transactions that occurred in two days, where 492 frauds out of 284,807 transactions were identified. The dataset has got the following features:
- V1, through to V28 (28 features): Represent the continous variables a credit card transaction recorded over the two days.
- Amount: respresents the credit card amount transacted.
- Time: represents the time a credit card transaction was executed across the two days.
- Class: this represents the target feature (binary classes where 0 respresents safe credidt card transactions while 1 represents fraudulent credit card transactions).
- Hence, dataset containing 31 features whereby 30 being explanatory features.
Dataset is loaded -- creating a DataFrame using the Pandas library through a read_csv() method.
- df.columns: nowing the column labels.
- df.shape: checks for number of rows and columns.
- df.sample(n): provides a random n rows of DataFrame.
- df.head(): prints the first five rows of the DataFrame.
- df.tail(): prints the last five rows of the DataFrame.
Handling the Imbalanced Dataset Right Away to Avoid issues when performing EDA whereby the Synthetic Minority Over-sampling Technique (SMOTE) is preferred
- SMOTE is a technique used to address class imbalance in machine learning datasets.
- Class imbalance: occurs when one class of the target variable has significantly fewer samples compared to another class, which can lead to a biased or poorly performing model.
- SMOTE is a popular method for addressing this issue as explained below:
- Identify the Minority Class: In a dataset with class imbalance, SMOTE focuses on the minority class.
- Generate Synthetic Samples: SMOTE works by generating synthetic samples for the minority class. It does this by selecting a sample from the minority class and finding its k-nearest neighbors within that class.
- Interpolation: Once the nearest neighbors are identified, SMOTE creates synthetic samples by interpolating between the selected sample and its neighbors. The synthetic samples are created by selecting a fraction of the distance between the selected sample and each of its neighbors.
- Balance the Classes: By generating synthetic samples for the minority class, SMOTE helps balance the class distribution. This makes the dataset more balanced and prevents the model from being biased toward the majority class.
- After Experimenting both the Undersampling and OverSampling Methods/techniques, it turned out that SMOTE was working well on the model performance, hence chosen.
- df = pd.concat() method was applied.
- Used sv.analyze() method after importing the library sweetviz as sv.
- Then a report is stored using the show_notebook() method.
- Checking for Datatypes.
- Checking for Missing Values (Isnull).
- Checked for duplicates and unique values.
- Checked for features' Minimum and Maximum values.
- Conducted Time conversion to get the correct time format (from the numeric) to the date-time format using to_datetime() method.
- Visualized the Time column plotting a Histogram to find out the time distribution on transactions.
- Visualized transactions Amount to spot outliers.
- Visualized Transaction Amount vs Target ('Class') using Seaborn library.
- Visualized pairwise correlation across features.
- Visualized the distribution of the Class values using Matplotlib.pyplot as plt (pie chart) to confirm the imbalanced dataset.
Performing Feature Transformation as Preparation for the Machine Learning Model to Efficiently train:
- Converted Time to binary value 0 and 1 integer datatype after clustering into two
- After all features were in float and integer datatypes, realized all float datatypes were in range above 1 value, hence need for scaling [0 & 1].
- Except for Time and Class features, which already were in binary format with integer datatype, the rest of features required transformation by scalling down continuous values to limiting them to between 0 and 1 uning the MinMaxScaler() method supported by the sklearn.preprocessing library.
- A preprocessor variable for the ColumnTransformer was created as well before a Machine Learning Model being built.
Using train_test_split() method imported from sklearn.model_selection was able to store X_train, y_train, X_test, y_test sets
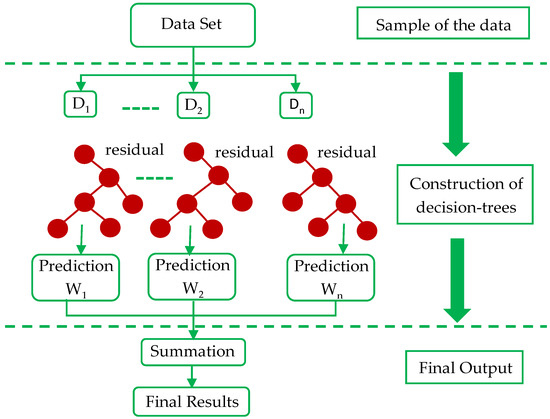
Given the nature of the problem statement, dataset, and required project procedures, the eXtreme Gradient Boost (XGBoost) model was selected among other models, which are capable of conducting predictions on binary classes. Below are a few summarized factors:
- Nature of Dataset (imbalanced) whereby XGBClassifier() performs overall best comparatively.
- Model flexibility in case:
- Regularization techniques required.
- Handling of missing data the case.
- Model interpretability ability to plot feature importance, confusion matrix, and classification report.
- Scalability of the model as the model could handle large dataset clients may have.
- Community support making reliability to access key information for future model usability and improvement.
Source: https://www.mdpi.com/2076-3417/12/4/2126
- Python Programming Language: for coding
- xgboost: for building the model classifier
- scikit-learn: for building the model estimator
- pandas: for loading dataset
- numpy: for numeric calcumlation across code snippets
- matplotlib: for image/plots/charts during training, and testing
- seaborn: for image/plots/charts -- confusion matrix
- argparse: provides command-line arguments and options in defining training scripts.
- The XGBoost classifier was built using the XGBClassier() methond imported from xgboost.
- From the imported Pipeline, the model pipeline was created using the pipeline() method where the preprocessing variable early created and the XGBoost classifiers wrapped in.
- The build XGBoost model pipleline was then training whereby X_train, y_train set wrapped in.
- Then prediction made (y_pred) of the model pipeline(X_test) applied
Checking for model Performance using different Peformance using pandas, accuracy_score, confusion_matrix, classification_report, matplotlib.pyplot, seaborn
- From both accuracy_score(y_train, y_train_pred) and accuracy_score(y_test, y_pred) methods, model accuracy at training and testing sets could be printed.
- Plotted confusion matrix.
- Printed a classification report where accuracy, precision, recall, and f1-score metrics are displayed.
- Plotting feature importance helped optiminzation of the model combination of features given the order of feature on the plot. Features way at the least order were dropped leading to a well performing model across performance metrics.
- Given this project, the minimum (model accuracy threshold) provided is 75%, from which the project should produce accuracy greater than. The model performance on local environment produced: training and testing precision (100%), recall (100%), and f1-score (100%) with both training and testing accuracy consistently at 100%. Hence, we good performing model in determining whether credit card transactions are fraudulents or not.
- On local environment, there was less hyperparameter fine-tuning improvement on the overall model performance. Hence, for efficiency and computional reasons, is important to use less parameters as optimal as possible as similar results will be achieved.
- The use of the model is very simple becuase it does not require hyperparamenter fine-tuning. Hence, computation time and cost minimized.
- Potential for Cost Savings: Using this model by the Bank may save money in preventing fraudulent transactions. It can also improve customer satisfaction by reducing the number of legitimate transactions incorrectly flagged as fraudulent.
- Model Resilience and reliability. This model may maintain its fraudulent predictive power (performance) on unseen data, which is important in a real-world setting where transactions distribution changes over time.
- Monitoring and Adaptation: Even with a high-performing model, it's essential to continuously monitor its performance and adapt it as needed. Fraudsters can change their tactics, and the model should be updated to address evolving threats related to creditcards' transactions.
- Customer Communication: In the banking domain, clear communication with customers is essential. Customers should be informed about the bank's fraud detection methods and how they can protect themselves. An overzealous fraud detection system may sometimes lead to customer inconvenience.
- Marketing Strategy: The bank may use the high-performance model promoting itself as a secure place to conduct financial transactions, emphasizing the commitment to protecting customers from fraud.
- Regulatory Compliance: Ensure that the model complies with relevant regulations and data privacy laws. Transparency in model development and usage is critical.
- Education and Training: Continuously educating and training the Bank employees on how to use and interpret the model results, as well as how to take appropriate actions when fraud is suspected.