-
Notifications
You must be signed in to change notification settings - Fork 5
Home
- Introduction
- System requirements
- Installation
- Concepts
- Integration steps
- Methods Available in IndoorLocationManager
- FAQs
The indoor location service and outdoor location service differ significantly. This is because most outdoor location services rely on GPS and other Global Navigation Satellite Systems (GNSS), which are obstructed by buildings' roofs and walls in the case of indoor location services. Consequently, GPS is not a suitable solution for our case study in terms of accuracy. To attain indoor location services, we utilize MistSDK, which employs BLE technology for indoor positioning, wayfinding systems, proximity notification, and other features.
MistSDK - Mist Software Development Kit.
By leveraging Mist's 16 vBLE antenna array access point, Mist SDK facilitates an indoor blue dot experience. With this SDK, you will have the ability to determine the user's location and deliver proximity-based notifications utilizing Mist's patented vBeacon technology.
Important features offered by our Mist SDK:
- Indoor Location
- Providing the coordinates in the map for your app to draw the blue dot location of the device.
- Virtual Beacon Notification
- A beacon, which is not physically present, but a virtual one. A virtual beacon that is added on the web portal and known by your app through the SDK. It provides notifications when the device is near the location of the virtual beacon.
- Virtual Zone Notification
- Zones are defined on the Mist portal as areas within a map. The SDK provides notifications on going into a zone.
- Wayfinding Path Information
- Wayfinding paths are defined on the Mist portal. The SDK provides the coordinate information from the current blue dot to the nearest point in the paths, through the shortest path to a given coordinate in the same map. This information can be used by the app to draw the shortest route a user can take to a destination.
-
Hardware Requirements:
- Mist Access Point with vBLE support (AP) - very important - Mist uses an AP with 16 vBLE antennas to get the position of the device on the floor.
- Android Mobile Device: Since the Android emulator doesn’t have Bluetooth support, it will not work properly. We need a physical device with BLE support for application testing and development with the SDK.
-
Software Requirements:
- Android Studio: 4.0 or later.
- Minimum Android SDK: API 26.
- Target Android SDK: API 34.
- Access to the Mist Account
- Mobile SDK secret
- Org ID
To get started with Maven Central, go to settings.gradle and in plugin management, update
pluginManagement {
repositories {
---
mavenCentral()
}
} And add the following to your app module build.gradle, this will take care of both the Mist Core SDK and the DR SDK.
implementation 'com.mist:core-sdk:5.0.0'Add import com.mist.android.*; to get started.
There are some mandatory steps to be taken initially to get started with an SDK:
- App Permissions
- Mobile SDK token
- Org ID
- Floor Plan (MistMap)
- Position Access Points (APs) in the floor plan
And the following are necessary on a need-based basis:
- Way-finding Paths
- Virtual Beacons
- Zones
- App Wakeup
The Mist SDK will require Bluetooth and location services to function on your device. Declare the following permissions in your application manifest file: For example
<uses-permission android:name="android.permission.ACCESS_NETWORK_STATE" />
<uses-permission android:name="android.permission.INTERNET" />
<uses-permission android:name="android.permission.BLUETOOTH_SCAN" />
<uses-permission android:name="android.permission.ACCESS_COARSE_LOCATION" />
<uses-permission android:name="android.permission.ACCESS_FINE_LOCATION" />
<uses-permission android:name="android.permission.BLUETOOTH" android:maxSdkVersion="30"/>
<uses-feature android:name="android.hardware.bluetooth_le"/>Now we are done with adding permissions. The next step is to create a Mobile SDK token to enroll the device in the Mist Cloud.
The Mobile SDK token is a secret key which can be created from the Mist portal. This key authenticates an SDK instance and identifies that it belongs to a specific organization in the Mist cloud.
Why is this Mobile SDK token needed?:
Mist provides the solution for indoor location services. With the Mobile SDK token we ensure that SDK instances are only used for specific organizations in the Mist cloud.
Token Creation Steps:
- To create a Mobile SDK token, you should have registered with the Mist portal
- Go to Organization --> Mobile SDK as
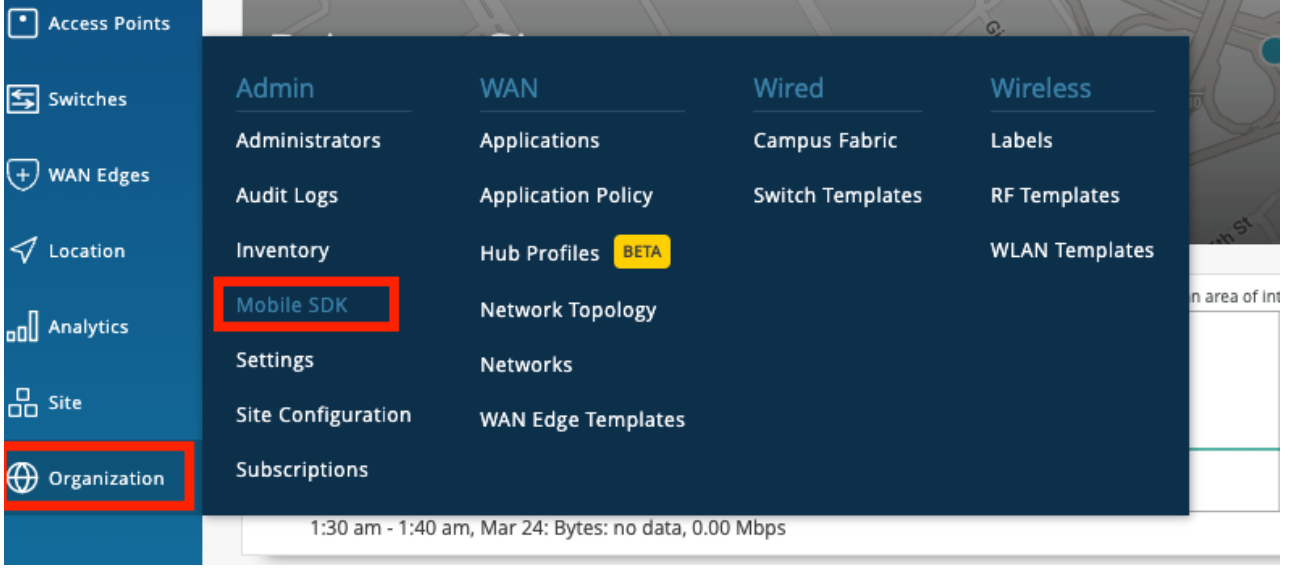
- Create a new invitation. It will ask for the organization name, and once you give the name and hit save, you will get your token. Refer to the image for a better understanding.

The Org ID is a unique identifier that links an SDK instance to a specific organization in the Mist cloud. It ensures that all operations and data are associated with the correct organization.
Steps to get Org ID:
- From the left menu, select Organization > Admin > Settings. The Organization ID appears near the top of the page. You can use the copy button to quickly copy this long string.

- Our goal is to provide indoor location services. This requires a map, specifically a floor plan.
- In the Mist portal, we can upload the floor plans. We call these the MistMaps.
Maps Supported
- Mist Map: Map type (jpeg, png, gif)
- Micello
- Jibestream
Conversion from Mist Coordinates to Other Maps Jibestream:
jibestreamX = (mistX1000)/mmpp
jibestreamY = (mistY1000)/mmpp
where mmpp is millimetres per pixel, which is specific to the map and will be provided by Jibestream itself
How to add the floor plan to the Mist Portal:
- Go to Location-> Live View. Here it will show all the existing floorplans, if there are none then it will tell you to add the floorplan with a button.

- To add a floor plan, click on the "Add Floor Plan" or "Import Floor Plan" button based on your requirements. You will be prompted to provide a name for the floor. Once you have entered the name, press "Enter,", and you will be asked to upload the floor plan image. Simply drag and drop the image into the designated area and click on the "Upload" button.
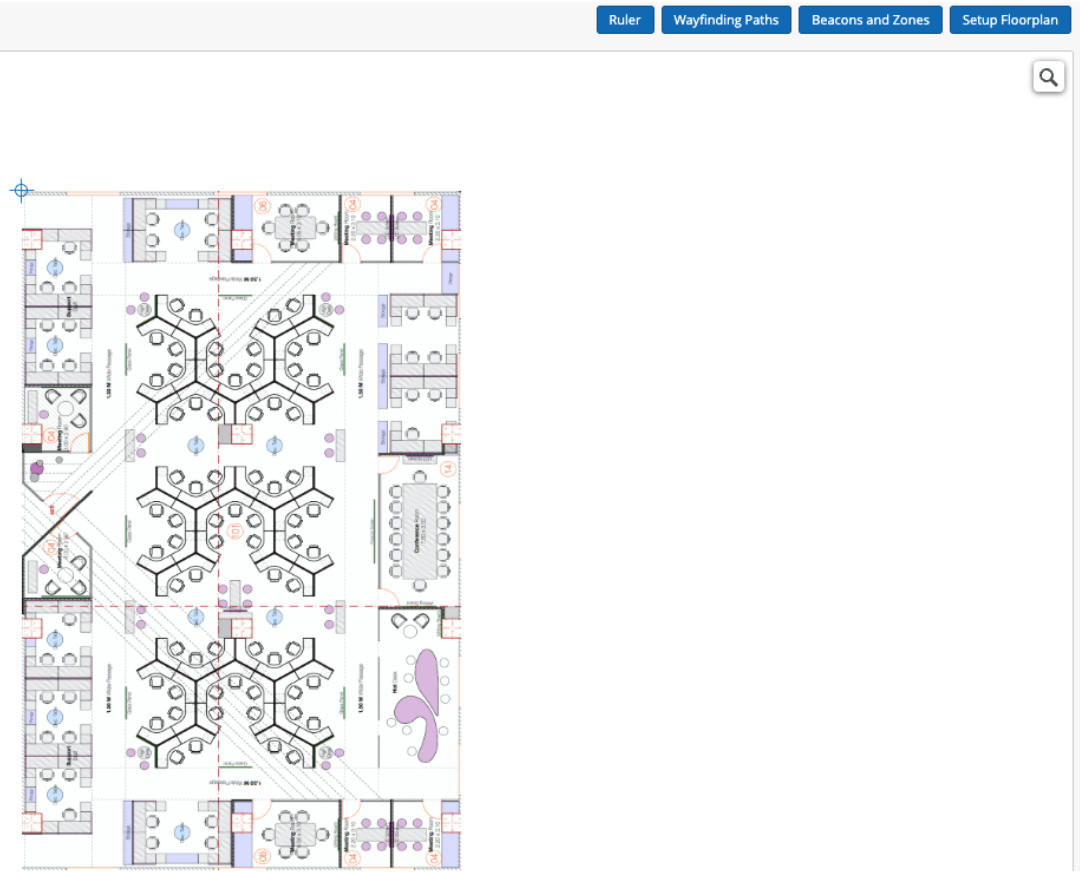
- The final step in configuring the floor plan is to add the PPM (pixels per meter) value. This indicates the distance in meters that each pixel on the floor plan represents.
Positioning the AP in the Mist Portal exactly as it is in the real world is crucial. Failing to do so will result in an inaccurate Mist Point.
How to position APs in the floor plan in the Mist Portal
Go to Location -> Live View -> Setup Floorplan, from here, you can see the list of APs that are claimed to that site and move them around to wherever you want.
This is one of the examples of floor plans with AP installed.
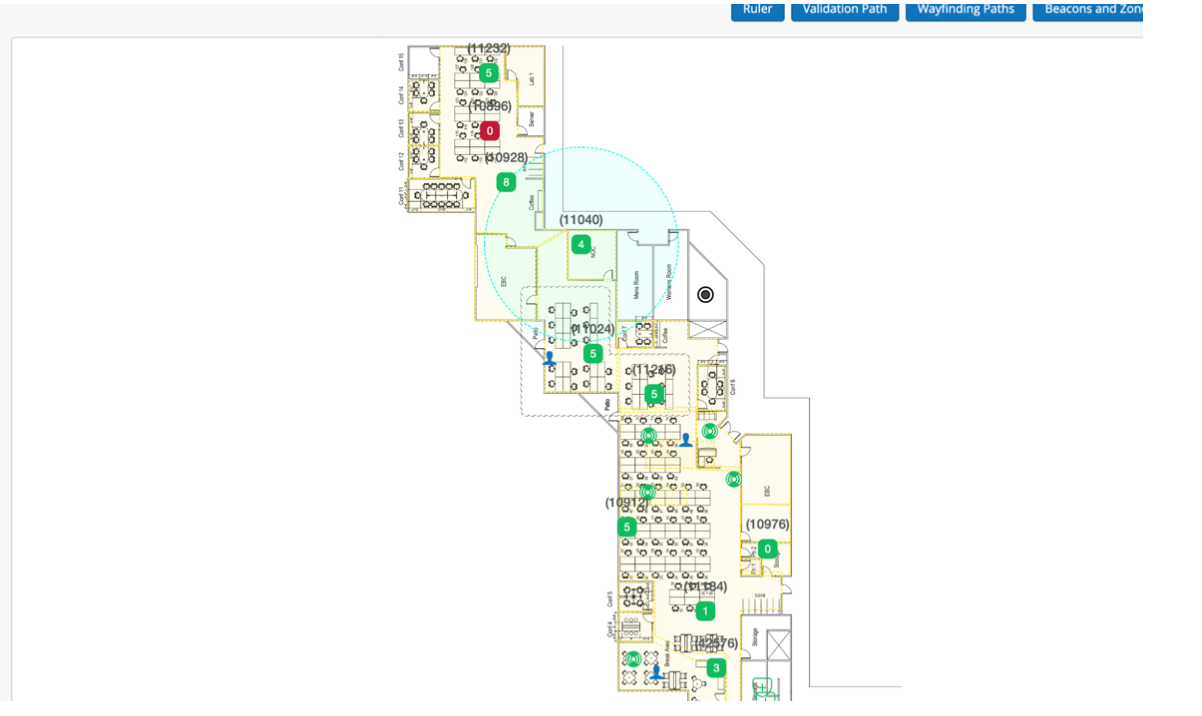
Wayfinding paths can be created to help the location estimate gravitate towards the paths drawn out. The wayfinding paths can also be used by your app to draw the shortest route for wayfinding. To generate the path, we can use the Mist portal and define the route directly on the map. For that
- Go to Location -> Live View -> Choose the floor plan
- Click the Wayfinding paths button
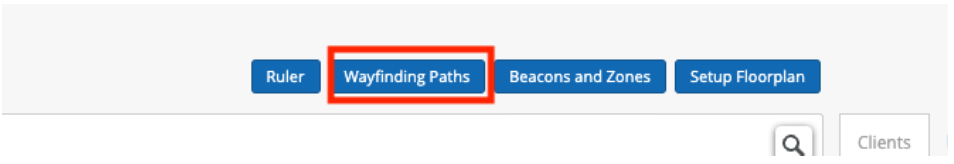
- You will see the following options:
- Draw paths in areas where there will be people walking and moving through; be sure to draw paths in every area where you intend to utilize the SDK clients. Make sure that all path segments are connected to each other.
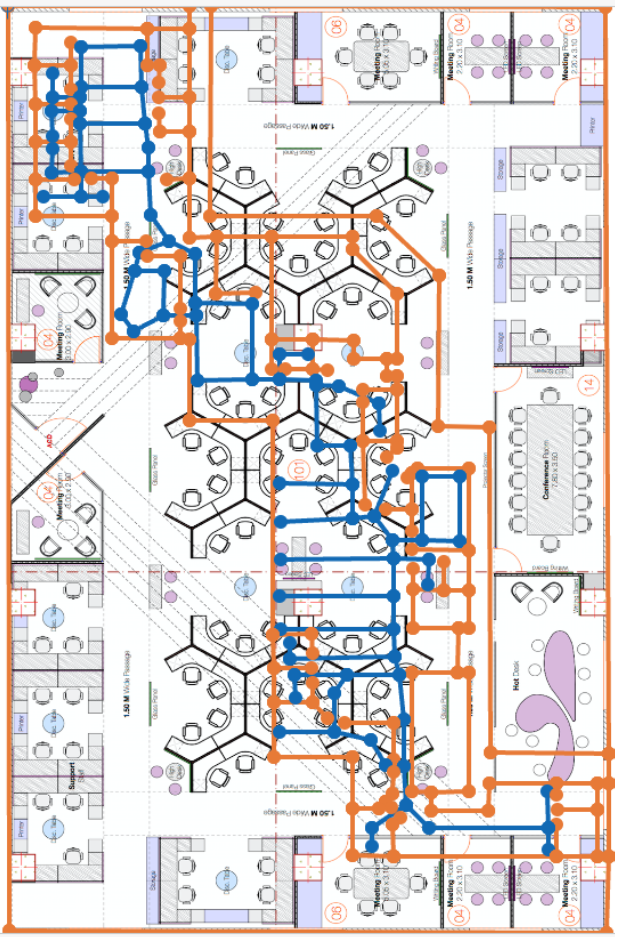
For more, go through https://www.mist.com/documentation/adding-wayfinding-paths/.
vBeacons are a Mist-patented technology that enables the provision of proximity-related information. The advantage of vBeacons is that they can be placed anywhere on the floor plan without concerns about battery life or relocation issues. Similar to real beacons, ranging APIs can be used for vBeacons. It’s important to note that these do not act as stand-ins for real beacons and are only for proximity-related notification information. Meaning that placing these vBeacons on your floorplan will not help increase accuracy.
To add the vBeacons,
- Go to Location->Live View-> select the floor plan->click the beacons and zones
- Now the user can create and move the vBeacon wherever he wants. All the green circles are vBeacons.

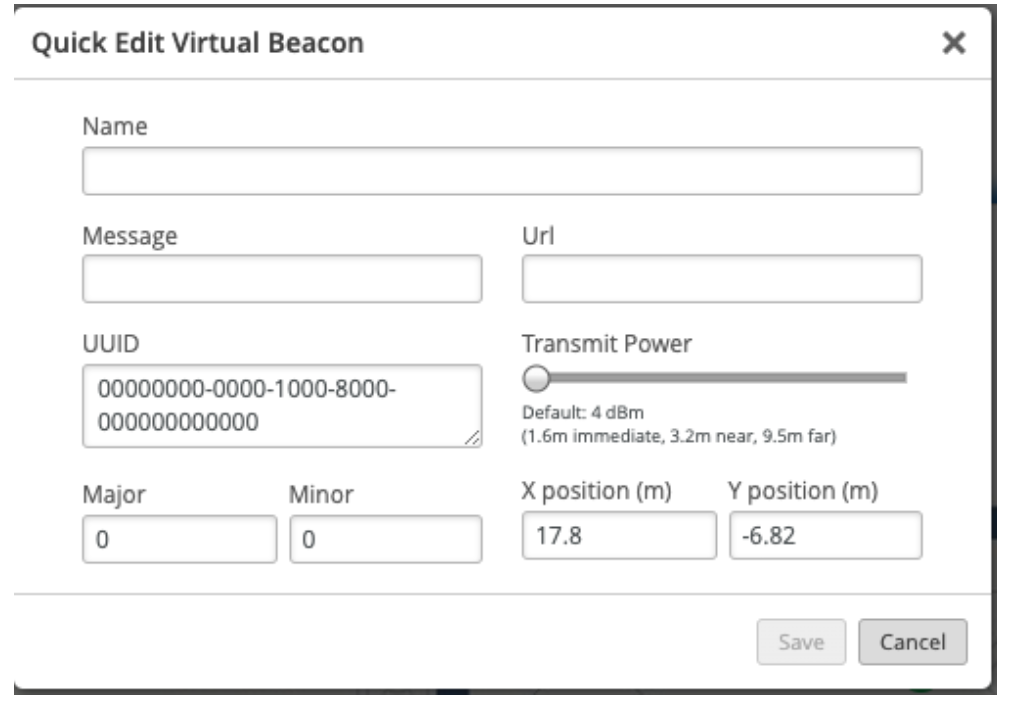
- Furthermore, we have the flexibility to customize the beacon according to your requirements. If you wish to remove a beacon, you can choose the "Remove" option, or if you want to make any modifications to the beacon, you can select the "Edit" option.
- If you intend to edit a beacon, you should fill in the necessary details in the edit popup and save the changes. On the other hand, if you wish to delete a beacon, simply click the "Delete" button.
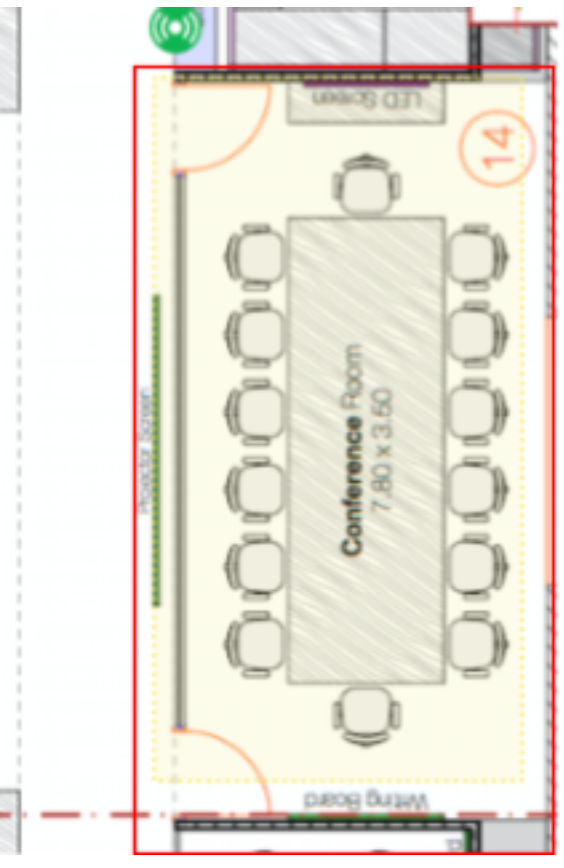
- A zone is a customized area defined on the Mist map that enables notifications to be sent to provide location-specific information to customers. We can send notifications when a user enters the specified zone in the Mist portal.
- To add zones, go to Location->Live View, select the floor plan, and click the beacons and zones.
- And click "Add Location Zone" and drag the area on the floor plan to create the zone.
- Refer to the highlighted area in the image for the zone.
Similar to virtual beacons, we have options to edit and delete the zones.
App wakeup refers to the act of bringing the app back to an active state when it enters the range of a registered beacon. This feature is primarily related to the app itself and not the Mist SDK. However, you can initiate the SDK in the background when you receive the callback in the killed state and utilize it for analytics purposes instead of navigation or location.
In Android, we are using ALTBeacon to achieve AppWakeup.
-
Import MistSDK
Java:
import com.mist.android.*;
Kotlin:
import com.mist.android.*
We can also import specific classes when needed.
import com.mist.android.IndoorLocationManager import com.mist.android.IndoorLocationCallback import com.mist.android.external.config.LogLevel import com.mist.android.external.config.MistConfiguration
-
Implement the current class with the IndoorLocationCallback interface.
Java:
public class MistSdkManager implements IndoorLocationCallback{ // }
Kotlin:
public class MistSdkManager: IndoorLocationCallback{ // }
-
Override all the required methods as stated in the IndoorLocationCallback so that the app will compile without any issues.
-
Create and initialize the SDK with the Mobile SDK token that you get through the token creation process.
Java:
private IndoorLocationManager indoorLocationManager = IndoorLocationManager.INSTANCE; //in between statement MistConfiguration mistConfiguration = new MistConfiguration( contextWeakReference.get(), <Access Token>, <Org ID>, <Client_UUID>, LogLevel.INFO, true, BatteryUsage.HIGH_BATTERY_USAGE_HIGH_ACCURACY );
Kotlin:
private var indoorLocationManager = IndoorLocationManager val mistConfiguration = MistConfiguration( context = this, token = <Access Token>, orgId = <Org ID> )
-
Users can specify the required Log levels, client uuid and Battery usage types in the mistConfiguration constructor. This is optional in Kotlin.
Example:
Kotlin:
val mistConfiguration = MistConfiguration( context = this, token = <Access Token>, enableLog = true, logLevel = LogLevel.INFO, batteryUsage = BatteryUsage.MEDIUM_BATTERY_USAGE_MEDIUM_ACCURACY, clientUUID = <client uuid>, orgId = <Org ID> )
Log levels:
The names of the different Log levels and their description are given below.logLevel Description DEBUG The DEBUG log level should be used for information that may be needed for diagnosing issues and troubleshooting or when running application in the test environment for the purpose of making sure everything is running correctly. INFO The standard log level indicating that something happened, the application entered a certain state. ERROR The log level that should be used when the application hits an issue preventing one or more functionalities from properly functioning. WARNING The log level that indicates that something unexpected happened in the application, a problem, or a situation that might disturb one of the processes. VERSBOSE Very detailed information, intended only for development. BatteryUsage types:
The names of the different Battery Usage types and their description are given below.batteryUsage Description LOW_BATTERY_USAGE_LOW_ACCURACY It consumes low battery power and gives the low accuracy. MEDIUM_BATTERY_USAGE_MEDIUM_ACCURACY It uses moderate batery consumption and gives medium accuracy. HIGH_BATTERY_USAGE_HIGH_ACCURACY It uses high battery conumption and also gives the high accuracy.
-
-
Start the location SDK.
Java:
indoorLocationManager.start(mistConfiguration, indoorLocationCallback);
Kotlin:
indoorLocationManager.start(mistConfiguration, indoorLocationCallback);
-
Once we have taken all the above steps, we will be able to get all the required information in the onReceiveEvent callback.
-
We need to implement onReceiveEvent callback to get all the required information
- onReceiveEvent
Required method to be overridden.
void onReceiveEvent(event : MistEvent)
There are several events which can be handled inside onReceiveEvent on need basis
OnReceivedClientInfo(val client: Client)
OnMapUpdate(val map: MistMap)
OnRelativeLocationUpdate(val point: MistPoint)
OnError(val error: ErrorType)
OnMessage(val message: MistMessage)
OnReceivedAllMaps(val maps: ArrayList<MistMap?>)
OnEnterZone(val zone: MistZone)
OnExitZone(val zone: MistZone)
OnUpdateVirtualBeaconList(val virtualBeacons: Array<MistVirtualBeacon?>?)
OnRangeVirtualBeacon(val virtualBeacon: MistVirtualBeacon)
OnConnectionStatus(val connectionStatus: ConnectionStatus)
| Events | Description |
|---|---|
| OnReceivedClientInfo | Event for client information when enrolment successful or client name has been updated from SDK |
| OnMapUpdate | Event for current map data |
| OnRelativeLocationUpdate | Event for current mist point |
| OnError | Event for any error occurred |
| OnMessage | Event for current sdk status |
| OnReceivedAllMaps | Event for all sites maps data |
| OnEnterZone | Event when the client enters the zone |
| OnExitZone | Event when the client exits the zone |
| OnUpdateVirtualBeaconList | Event for all Virtual Beacons for the current map |
| OnRangeVirtualBeacon | Event when the client is in the range of a VirtualBeacon |
| OnConnectionStatus | Event for connection status |
Example:
onReceiveEvent
In this method, user can handle events from SDK for different type of MistEvent.
Example:
Java:
@Override
public void onReceiveEvent(@NonNull MistEvent event) {
if(event instanceof OnReceivedClientInfo){
Log.d("OnReceivedClientInfo", "Client " + ((OnReceivedClientInfo) event).getClient());
}
else if (event instanceof OnMapUpdate){
Log.d("OnMapUpdate", "current map detail" + ((OnMapUpdate) event).getMap());
}
else if (event instanceof OnRelativeLocationUpdate){
Log.d("OnRelativeLocationUpdate", "relativeLocation" + ((OnRelativeLocationUpdate) event).getPoint());
}
else if (event instanceof OnError){
Log.d("OnError", "Error type " + ((OnError) event).getError());
}
else if(event instanceof OnMessage){
Log.d("OnMessage", "sdk status" + ((OnMessage) event).getMessage());
}
else if (event instanceof OnReceivedAllMaps){
for (MistMap map : ((OnReceivedAllMaps) event).getMaps()){
Log.d("Map Name", map.toString());
}
}
else if (event instanceof OnEnterZone){
Log.d("OnEnterZone", "region " + ((OnEnterZone) event).getZone());
}
else if (event instanceof OnExitZone){
Log.d("OnExitZone", "region " + ((OnExitZone) event).getZone());
}
else if (event instanceof OnUpdateVirtualBeaconList) {
if(((OnUpdateVirtualBeaconList) event).getVirtualBeacons()!=null){
for(MistVirtualBeacon vbeacon : ((OnUpdateVirtualBeaconList) event).getVirtualBeacons()){
Log.d("OnUpdateVirtualBeaconList", vbeacon.toString());
}
}
}
else if (event instanceof OnRangeVirtualBeacon){
Log.d("OnRangeVirtualBeacon", "ranging beacon " + ((OnRangeVirtualBeacon) event).getVirtualBeacon());
}
}Kotlin:
override fun onReceiveEvent(event: MistEvent) {
when(event){
is MistEvent.OnReceivedClientInfo ->{
Log.d("OnReceivedClientInfo", "Client:" + event.client.toString())
}
is MistEvent.OnMapUpdate -> {
Log.d("OnMapUpdate", "current map detail" + event.map.toString())
}
is MistEvent.OnRelativeLocationUpdate -> {
Log.d("OnRelativeLocationUpdate", "relativeLocation" + event.point.toString())
}
is MistEvent.OnError -> {
Log.d("OnError", "Error" + event.error.toString() )
}
is MistEvent.OnMessage -> {
Log.d("OnMessage", "SDK status" + event.message.toString())
}
is MistEvent.OnReceivedAllMaps -> {
for (map in event.maps){
Log.d("Map Name", map.toString())
}
}
is MistEvent.OnEnterZone -> {
Log.d("OnEnterZone", "region" + event.zone.toString())
}
is MistEvent.OnExitZone -> {
Log.d("OnExitZone", "region" + event.zone.toString())
}
is MistEvent.OnUpdateVirtualBeaconList -> {
if(event.virtualBeacons!=null) {
for (vbeacon in event.virtualBeacons){
Log.d("OnUpdateVirtualBeaconList", vbeacon.toString())
}
}
}
is MistEvent.OnRangeVirtualBeacon -> {
Log.d("OnRangeVirtualBeacon", "ranging beacon" + event.virtualBeacon.toString())
}
}
}Mist Events
User can handle these events inside onReceiveEvent callback from SDK.
OnRelativeLocationUpdate
This event will get triggered, when relative postions of the client is updated. The main purpose of this sub event is to provide a relativeLocation of type MistPoint, which provides detailed information about the current location of the device.
Java:
@Override
public void onReceiveEvent(@NonNull MistEvent event) {
if (event instanceof OnRelativeLocationUpdate){
Log.d("OnRelativeLocationUpdate", "relativeLocation" + ((OnRelativeLocationUpdate) event).getPoint());
}
}Kotlin:
override fun onReceiveEvent(event: MistEvent) {
when(event){
is MistEvent.OnRelativeLocationUpdate -> {
Log.d("OnRelativeLocationUpdate", "relativeLocation" + event.point.toString())
}
}
}MistPoint
| Attribute | Data Type | Description |
|---|---|---|
| x | double | X-coordinate of the MistPoint in the MistMap. |
| y | double | Y-coordinate of the MistPoint in the MistMap. |
| hasMotion | boolean | Indicates if the MistPoint has motion. |
| speed | double | Speed of the MistPoint. |
| mstPointType | MSTPointType | Type of the MistPoint (Cloud, Device, or LastKnown). |
| latency | double | Latency of the MistPoint. |
| heading | double | Heading of the MistPoint. |
| map | MistMap | The MistMap that the MistPoint belongs to. |
| lat | double | Latitude of the MistPoint in the real-world. |
| lon | double | Longitude of the MistPoint in the real-world. |
OnMapUpdate.
- This event will be triggered in the following situations.
- initially when the mobile receives relative location
- And the current floor plan has been changed (if the user moves from one floor to another).
- This event can be handled inside onReceiveEvent callback
Java:
@Override
public void onReceiveEvent(@NonNull MistEvent event) {
if (event instanceof OnMapUpdate){
Log.d("OnMapUpdate", "current map detail" + ((OnMapUpdate) event).getMap());
}
}Kotlin:
override fun onReceiveEvent(event: MistEvent) {
when(event){
is MistEvent.OnMapUpdate -> {
Log.d("OnMapUpdate", "current map detail" + event.map.toString())
}
}
}MistMap
| Name | Data Type | Description |
|---|---|---|
| name | String | The name of the map. |
| type | String | The type of the map. |
| width | Integer | The width of the map in pixels. |
| height | Integer | The height of the map in pixels. |
| widthM | Double | The width of the map in meters. |
| heightM | Double | The height of the map in meters. |
| ppm | Double | The number of pixels per meter. |
| id | String | The unique ID of the map. |
| siteId | String | The ID of the site that the map belongs to. |
| orgId | String | The ID of the organization that the map belongs to. |
| createdTime | Integer | The timestamp of when the map was created. |
| modifiedTime | Integer | The timestamp of when the map was last modified. |
| url | String | The URL of the map. |
| thumbnailUrl | String | The URL of the map's thumbnail image. |
| orientation | Integer | The orientation of the map. |
| wayfinding | Wayfinding | The wayfinding information for the map. |
| latLongBR | LatLong | The latitude and longitude of the bottom right corner of the map. |
| latLongTL | LatLong | The latitude and longitude of the top left corner of the map. |
| wayfindingPath | MistPath | The path information for the map's wayfinding. |
| sitesurveyPath | ArrayList | The path information for the map's site survey. |
| wallPath | MistPath | The path information for the map's wall. |
| occupancyLimit | long | The occupancy limit for the map. |
| intendedCoverageAreas | List | A list of the intended coverage areas for the map. |
| isLocked | boolean | Whether or not the map is locked. |
MistPath
| Name | Data Type | Description |
|---|---|---|
| coordinate | String | The coordinate of the MistPath. |
| name | String | The name of the MistPath. |
| nodes | List | The list of nodes that make up the path. |
| pathID | String | The ID of the MistPath. |
Wayfinding
| Name | Data Type | Description |
|---|---|---|
| default | String | The default wayfinding method. |
| jibestream | Jibestream | The Jibestream wayfinding information. |
| micello | Micello | The Micello wayfinding information. |
Jibestream
| Name | Data Type | Description |
|---|---|---|
| venueId | String | The ID of the Jibestream venue. |
| mapId | String | The ID of the Jibestream map. |
| ppm | String | The number of pixels per meter for the Jibestream map. |
| clientId | String | The client ID for the Jibestream API. |
| clientSecret | String | The client secret for the Jibestream API. |
| customerId | String | The customer ID for the Jibestream API. |
| endpointUrl | String | The endpoint URL for the Jibestream API. |
| mmpp | String | The mmpp value of the Jibestream map |
| id | String | The unique identifier of the Jibestream wayfinding configuration |
Micello
| Name | Data Type | Description |
|---|---|---|
| accountKey | String | The account key of the map |
| mapId | String | The ID of the map |
| scaleRatio | Double | The scale ratio of the map |
| drawingId | String | The ID of the drawing in the map |
| geoId | Object | The ID of the geographical location in the drawing |
| defaultLevelId | String | The ID of the default level in the map |
| cid | String | The ID of the category associated with the drawing |
| did | String | The ID of the department associated with the drawing |
| lid | String | The ID of the level associated with the drawing |
| imageUrl | String | The URL of the image associated with the drawing |
| zoomLevel | Object | The zoom level of the map |
| enablePOI | Object | Indicates if points of interest are enabled for the map |
| transformParams | TransformParams | The parameters used for transforming the map image to its correct size |
LatLong
| Name | Data Type | Description |
|---|---|---|
| lat | Double | The latitude value of a location |
| lng | Double | The longitude value of a location |
PathNode
| Name | Data Type | Description |
|---|---|---|
| name | String | The name of the node. |
| position | NodePosition | The position of the node. |
| edges | Map<String, String> | A map containing the edges of the node. The keys are the IDs of the nodes that are connected to this node, and the values are the IDs of the edges connecting the nodes. |
NodePosition
| Name | Data Type | Description |
|---|---|---|
| x | double | The X-coordinate of the node position. |
| y | double | The Y-coordinate of the node position. |
TransformParams
| Name | Data Type | Description |
|---|---|---|
| lid | Integer | Level ID |
| transform | List | List of transformation parameters |
| did | Integer | Drawing ID |
| mercToNat | List | List of mercator-to-native transformation values |
| cid | Integer | Coordinate ID |
OnError
This event will get triggered, if the SDK faces any error rather than getting any positive response. And it will help us by giving us two values.
- errorType of type ErrorType Enum.
Java:
@Override
public void onReceiveEvent(@NonNull MistEvent event) {
if (event instanceof OnError){
Log.d("OnError", "Error type " + ((OnError) event).getError());
}
}Kotlin:
override fun onReceiveEvent(event: MistEvent) {
when(event){
is MistEvent.OnError -> {
Log.d("OnError", "Error" + event.error.toString() )
}
}
}ErrorType
| Error | Description |
|---|---|
| missingURL | url is missing |
| jsonEncodingFailed | json encoding failed. |
| customeEncodingFailed | encoding failed |
| invalidToken | Mist SDK token either empty or invalid |
| invalidRequest | request is invalid |
| hostEnvironmentIsNil | environment host url is nil |
| unknownHost | unknown environment |
| valueIsMissing | Data is missing |
| notConnected | Mist SDK is not connected to cloud please make sure SDK is started and the connection status is true before using this feature |
| mapDataNotAvailable | Map data is not available please use this feature after you get map info from onMapUpdated |
| getInstanceNotCalled | Please use the latest start(config) method or if you are still using older deprecated method please first call getInstance before calling start |
| jmapConfigMissing | Jmap config data missing please check third party integration of your map in mist portal |
| failedToEnroll | Enrollment failed |
| noBleFound | MistSDK is stopped. No vBLE Beacon found for last 5 minutes. Please restart the sdk after some time. |
| operationalFileRelated | Operationally Disabled |
| noMistBeacon | PreCheck - No Mist BLE Beacon found! |
OnConnectionStatus
This event will be triggered, if the SDK is successfully connected. It will give the value connectionStatus of type ConnectionStatus Enum.
Example:
Java:
Java:
@Override
public void onReceiveEvent(@NonNull MistEvent event) {
if (event instanceof OnConnectionStatus){
}
}Kotlin:
override fun onReceiveEvent(event: MistEvent) {
when(event){
is MistEvent.OnConnectionStatus -> {
}
}
}As we already went through, a zone is a custom area defined on the Mist map to get notification to provide vicinity-related information to your customer. And this event will get triggered when a device enters/exits the defined zone area in the Mist portal.
OnEnterZone
This event will be triggered when the app enters our monitoring region (the area we marked as a zone in our MistMap).
Java:
@Override
public void onReceiveEvent(@NonNull MistEvent event) {
if (event instanceof OnEnterZone){
Log.d("OnEnterZone", "region " + ((OnEnterZone) event).getZone());
}
}Kotlin:
override fun onReceiveEvent(event: MistEvent) {
when(event){
is MistEvent.OnEnterZone -> {
Log.d("OnEnterZone", "region" + event.zone.toString())
}
}
}OnExitZone
This event will be triggered when the app exits our monitoring region (the area we marked as a zone in our MistMap). Both above events give us a mistZone object of type MistZone.
Java:
@Override
public void onReceiveEvent(@NonNull MistEvent event) {
if (event instanceof OnExitZone){
Log.d("OnExitZone", "region " + ((OnExitZone) event).getZone());
}
}Kotlin:
override fun onReceiveEvent(event: MistEvent) {
when(event){
is MistEvent.OnExitZone -> {
Log.d("OnExitZone", "region" + event.zone.toString())
}
}
}MistZone
| Name | Data Type | Description |
|---|---|---|
| timestamp | String | The timestamp of the zone event |
| origin | Integer | The origin of the zone event |
| level | Integer | The level of the zone event |
| recipient | String | The recipient of the zone event |
| recipientID | Object | The ID of the recipient of the zone event |
| name | String | The name of the zone event |
| userID | String | The user ID associated with the zone event |
| orgID | String | The organization ID associated with the zone event |
| siteID | String | The site ID associated with the zone event |
| mapID | String | The map ID associated with the zone event |
| clientType | String | The client type associated with the zone event |
| isRandom | Boolean | Whether the zone event is random or not |
| zoneID | String | The zone ID associated with the zone event |
| zonePosition | ZonePosition | The position of the zone |
| trigger | String | The trigger associated with the zone event |
| time | String | The time of the zone event |
| sinceTime | String | The time since the zone event |
| timeEpoch | Integer | The epoch time of the zone event |
| sinceTimeEpoch | Integer | The epoch time since the zone event |
| sessionID | String | The session ID associated with the zone event |
| duration | Integer | The duration of the zone event |
ZonePosition
| Name | Data Type | Description |
|---|---|---|
| x | Double | The x coordinate of the zone position |
| y | Double | The y coordinate of the zone position |
| z | Double | The z coordinate of the zone position |
OnReceivedAllMaps
- This event returns us maps for all sites in the entire organization, when SDK is initialized. It gives us the array of maps, which is supposed to be of the MistMap type (properties were explained in detail in the OnMapUpdated event explanation).
Java:
@Override
public void onReceiveEvent(@NonNull MistEvent event) {
if (event instanceof OnReceivedAllMaps){
for (MistMap map : ((OnReceivedAllMaps) event).getMaps()){
Log.d("Map Name", map.toString());
}
}
}Kotlin:
override fun onReceiveEvent(event: MistEvent) {
when(event){
is MistEvent.OnReceivedAllMaps -> {
for (map in event.maps){
Log.d("Map Name", map.toString())
}
}
}
}As we already know, vBeacons can provide proximity-related information, and the good thing is that you can move this vBeacon wherever you want to place it on your floorplan and never have to worry about any battery or relocation problems. It will work the same way as a physical beacon.
OnRangeVirtualBeacon
This event returns the current ranging beacon around user.
Java:
@Override
public void onReceiveEvent(@NonNull MistEvent event) {
if (event instanceof OnRangeVirtualBeacon){
Log.d("OnRangeVirtualBeacon", "ranging beacon " + ((OnRangeVirtualBeacon) event).getVirtualBeacon());
}
}Kotlin:
override fun onReceiveEvent(event: MistEvent) {
when(event){
is MistEvent.OnRangeVirtualBeacon -> {
Log.d("OnRangeVirtualBeacon", "ranging beacon" + event.virtualBeacon.toString())
}
}
}OnUpdateVirtualBeaconList
This event returns all the available virtual beacons placed on the floorplan when SDK is initialized.
Java:
@Override
public void onReceiveEvent(@NonNull MistEvent event) {
if (event instanceof OnUpdateVirtualBeaconList) {
if(((OnUpdateVirtualBeaconList) event).getVirtualBeacons()!=null){
for(MistVirtualBeacon vbeacon : ((OnUpdateVirtualBeaconList) event).getVirtualBeacons()){
Log.d("OnUpdateVirtualBeaconList", vbeacon.toString());
}
}
}
}Kotlin:
override fun onReceiveEvent(event: MistEvent) {
when(event){
is MistEvent.OnUpdateVirtualBeaconList -> {
if(event.virtualBeacons!=null) {
for (vbeacon in event.virtualBeacons){
Log.d("OnUpdateVirtualBeaconList", vbeacon.toString())
}
}
}
}
}It returns the object or array of objects of the type MistVirtualBeacon.
Properties of MistVirtualBeacon
MistVirtualBeacon
| Name | Data Type | Description |
|---|---|---|
| orgID | String | ID of the organization where the virtual beacon belongs |
| siteID | String | ID of the site where the virtual beacon belongs |
| mapID | String | ID of the map where the virtual beacon is located |
| vbID | String | ID of the virtual beacon |
| vbUUID | String | UUID of the virtual beacon |
| vbMajor | Long | Major value of the virtual beacon |
| vbMinor | Long | Minor value of the virtual beacon |
| power | String | Power status of the virtual beacon |
| power_mode | String | Power mode of the virtual beacon |
| message | String | Message associated with the virtual beacon |
| created_time | Long | Timestamp when the virtual beacon was created |
| modified_time | Long | Timestamp when the virtual beacon was last modified |
| tag_id | String | Tag ID associated with the virtual beacon |
| name | String | Name of the virtual beacon |
| url | String | URL associated with the virtual beacon |
| position | BeaconPosition | Position of the virtual beacon in 3D space |
| additionalInfo | AdditionalInfo | Additional information associated with the virtual beacon |
BeaconPosition
| Name | Data Type | Description |
|---|---|---|
| x | Double | X-coordinate of the virtual beacon position |
| y | Double | Y-coordinate of the virtual beacon position |
| z | Double | Z-coordinate of the virtual beacon position |
AdditionalInfo
| Name | Data Type | Description |
|---|---|---|
| userID | String | ID of the user associated with the virtual beacon |
| clientType | String | Type of the client device used to detect the virtual beacon |
| isRandom | Boolean | Flag indicating if the virtual beacon was detected randomly |
| proximity | String | Proximity status of the virtual beacon |
| distance | Double | Distance of the virtual beacon from the client device |
| rssi | Double | Received Signal Strength Indication of the virtual beacon |
| timestamp | String | Timestamp when the virtual beacon was detected |
| orientation | Long | Orientation of the client device when the virtual beacon was detected |
| direction | String | Direction of the client device when the virtual beacon was detected |
| timeEpoch | Long | Epoch time when the virtual beacon was detected |
| timezone | String | Timezone of the client device when the virtual beacon was detected |
| tzoffset | Long | Timezone offset of the client device when the virtual beacon was detected |
| origin | Long | Origin ID of the virtual beacon |
| level | Long | Level ID of the virtual beacon |
| recipient | String | Recipient of the virtual beacon message |
| recipientID | Object | ID of the recipient of the virtual beacon message |
-
And finally, we simply call the stop function in the indoor Location manager to stop the SDK.
a. Java:
indoorLocationManager.stop();b. Kotlin:
indoorLocationManager.stop()
1. public void start(MistConfiguration mistConfiguration, IndoorLocationCallback indoorLocationCallback);
2. public void stop();
3. public List<Node> getWayFindingPathTo(Position destination);
5. public void saveClientInformation(String clientName);
6. public void getClientInformation();
7. public void setBatteryUsage(BatteryUsage batteryUsage)
8. public BatteryUsage getBatteryUsage()
9. public String clientUUID
- This method will start the Mist SDK.
- It will take an IndoorLocationCallback as a parameter.
- And it returns void.
- Usage:
- Java:
indoorLocationManager.start(mistConfiguration, indoorLocationCallback);
- Kotlin:
indoorLocationManager.start(mistConfiguration, indoorLocationCallback)
- This method will stop MistSDK.
- It doesn’t take any arguments and returns void.
- Usage:
- Java:
indoorLocationManager.stop();
- Kotlin:
indoorLocationManager.stop()
- This method will return a list of nodes to be traversed when we want to draw the path towards the destination.
- We should pass the destination (an object of type Position) as an argument.
- It will return a sequence of nodes to be traversed in an array format of type [Node].
- Usage:
- Java:
List<Node> nodes = indoorLocationManager.getWayFindingPathTo(new Position(10.0,10.0));
- Kotlin:
var nodes = indoorLocationManager.getWayFindingPathTo(Position(10.0,10.0))
- This method saves the client information to the Mist server (the client is the current user in the session).
- The user can send his name to the server via this method, and the SDK will invoke the API to update the username on the server. After this process, we can easily find the user on the map via this name.
- It takes the username as parameter. It doesn’t return anything. Since this is an asynchronous function, we get the result from the sdk in the form of in the form of OnReceivedClientInfo Event .
- Usage:
- Java:
indoorLocationManager.saveClientInformation("<username>");
- Kotlin:
indoorLocationManager?.saveClientInformation("<username>")
- and the result will be returned in OnReceivedClientInfo Event.
- It fetches the client information from the server and returns it to the application in the form of OnReceivedClientInfo Event
- Usage:
- Java:
indoorLocationManager.getClientInformation();
- Kotlin:
indoorLocationManager.getClientInformation()
- This variable will give us the current Mist User UUID from the sdk.
- Java:
String uuid = indoorLocationManager.clientUUID;
- Kotlin:
String uuid = indoorLocationManager.clientUUID
For further questions please reach out to [email protected]