dynamodblock is a pure Python library that implements a distributed blocking mechanism for AWS Lambda using DynamoDB as a backend. It is useful for ensuring exclusive execution of concurrent tasks, avoiding collisions in concurrent executions, and has millisecond accuracy.
The library supports configurable TTL, retry logic with backoff, customizable timeouts, and operates in the time zone of your choice. It also integrates seamlessly with CloudWatch, enabling detailed logging for monitoring and debugging.
This library does not handle AWS credentials or access keys, you need to provide an already instantiated boto3.resource("dynamodb").Table("your_lock_table_name") with your credentials data
What's new in v1.0.6 - 14/May/2025
- Up until version 1.0.5, the release_all_locks() function returned a generator. Starting with version 1.0.6, you can simply call lock.release_all_locks() without any issues.
- The get_all_locks() function continues to return as a generator, that is, to get all the items at once you need to call it as list(lock.get_all_locks()).
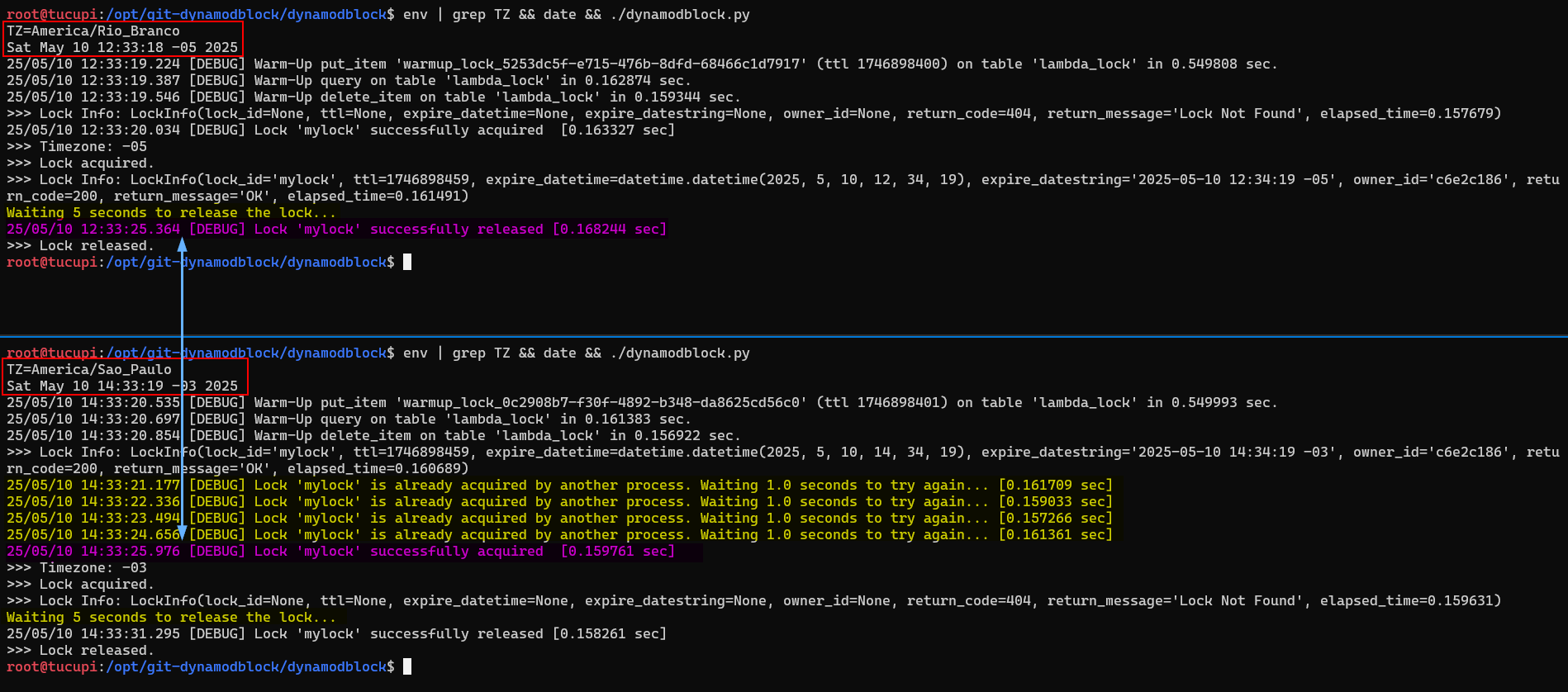
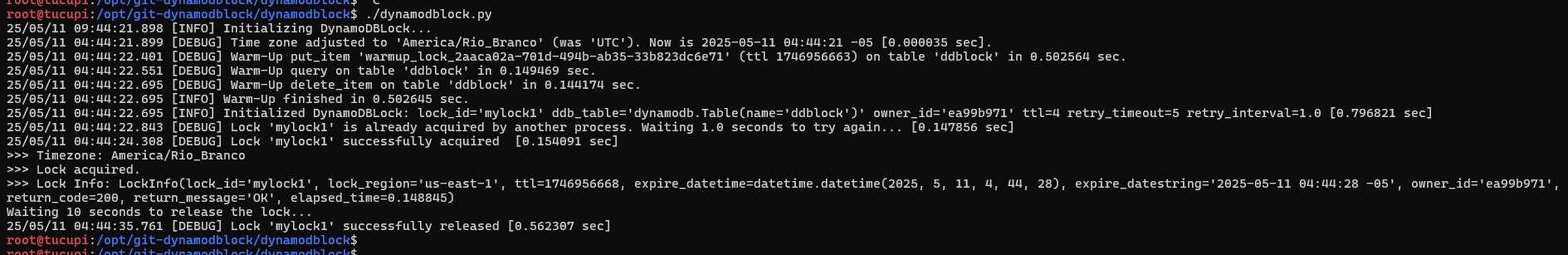
Here we have 2 sessions with timezones 2 hours apart, competing for a lock with executions 1 second after each other. The lock has 10 seconds of retries with a 1 second interval between each attempt. If the initial lock remained active for 5 seconds, the subsequent lock will be able to perform acquire() before the 10 second timeout.
Below we see a timezone change and a complete and successful execution.
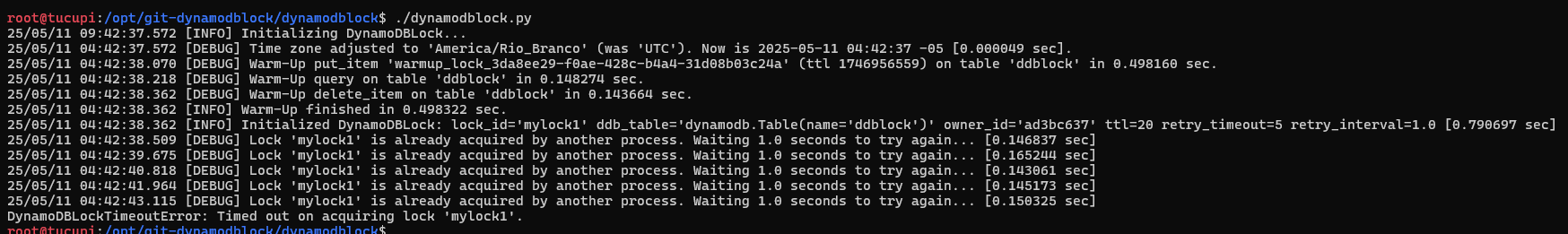
An another example of retrying to acquire the lock but ending unsuccessfully, with a timeout error that can be handled through DynamoBDLock exceptions.
pip install dynamodblock- Python 3.10+
- boto3 (of course)
- A DynamoDB table with a primary key
lock_id(string) - Avoid using global tables due to the replication time between them, which although considered low, there is a small difference of milliseconds that can cause overlapping locks.
import boto3
from dynamodblock import DynamoDBLock
# Initialize DynamoDB table resource
client = boto3.resource("dynamodb")
table = client.Table("locks-table")
# Create a lock
lock = DynamoDBLock(
lock_id="my-task-lock",
dynamodb_table_resource=table,
lock_ttl=30, # seconds
retry_timeout=5,
retry_interval=0.5,
verbose=True,
)
# Use as context manager
with lock.acquire():
# Critical section
print("running with lock...")Other ways to use DynamoDBLock:
import boto3
from dynamodblock import DynamoDBLock
client = boto3.resource("dynamodb")
table = client.Table("locks-table")
with DynamoDBLock(lock_id='my_lock',dynamodb_table_resource=table) as lock:
# Critical section
do_something_exclusive()
my_lock = DynamoDBLock(lock_id='my_lock',dynamodb_table_resource=table)
try:
my_lock.acquire()
# Critical section
do_something_exclusive()
finally:
my_lock.release()An example of a lambda function code for testing
#!/usr/bin/env python3
# -*- coding: utf-8 -*-
import os, warnings
os.environ['PYTHONWARNINGS'] = "ignore"
warnings.simplefilter("ignore")
import boto3, time
from dynamodblock import DynamoDBLock
class lambda_log:
def __init__(self,prefix:str):
self.prefix = prefix
def info(self,msg):
print(f"[{self.prefix}] {str(msg)}",flush=True)
def lambda_handler(event, context):
log = lambda_log(context.aws_request_id[:8])
ddb_table = boto3.resource('dynamodb').Table('ddblock')
lock = DynamoDBLock(lock_id='mylock',dynamodb_table_resource=ddb_table,owner_id=context.aws_request_id[:8],lock_ttl=20,warmup=True,
verbose=True,debug=True,log_prefix=f"[{context.aws_request_id[:8]}] ",timezone="America/Sao_Paulo")
with lock.acquire():
log.info(f"Sleeping for 5 seconds")
time.sleep(5)
log.info(f"ALL DONE!") Use this structure in your lambda function code. You can run pip install dynamodblock -t ./ to install the library in your current directory.
├── dynamodblock
│ ├── __init__.py
│ └── dynamodblock.py
└── lambda_function.py
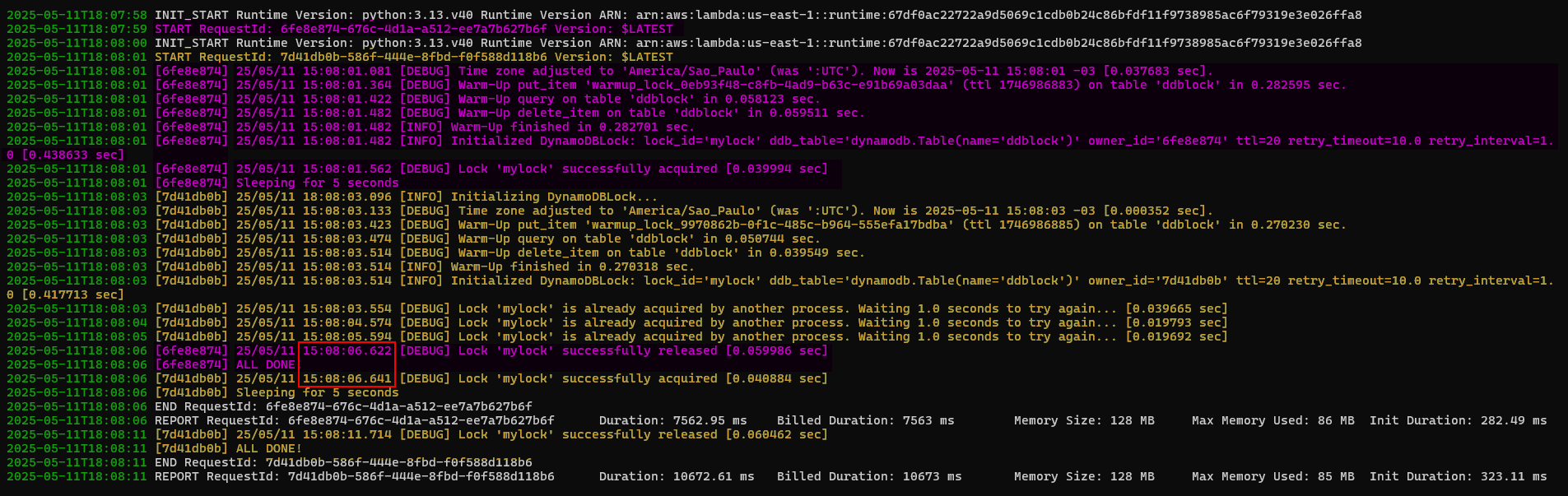
And below is a screenshot of CloudWatch logs from two concurrent executions (using the code above) 2 seconds apart
def get_lock_info(self)->namedtuple
Returns a named LockInfo with the lock information. TTL is used by DynamoDB to expire records, and TTL_PRECISE is used by DynamoDBLock to ensure the accuracy of the lock written to the millisecond.
>>> my_lock_info = lock.get_lock_info()
>>> print(my_lock_info)
>>> LockInfo(lock_id='mylock1', lock_region='us-east-1', ttl=Decimal('1747211435'), ttl_precise=Decimal('1747211435.0648081'), expire_datetime=datetime.datetime(2025, 5, 14, 5, 30, 35, 64808), expire_datestring='2025-05-14 05:30:35.064808 -03', owner_id='28baf959', return_code=200, return_message='OK', elapsed_time=0.163222)
>>> print(my_lock_info.lock_id)
>>> 'mylock1'
>>> print(my_lock_info.owner_id)
>>> '88d6235e'def is_locked(self)->bool:
Is a PROPERTY. Return True if the lock is acquired by another process.
>>> print(lock.is_locked)
>>> Truedef get_owner_id(self)->str:
Return the owner_id of the lock.
>>> print(lock.get_owner_id())
>>> '88d6235e'def get_current_timezone(self)->str:
Return the current timezone string of the DynamoDBLock object.
>>> print(lock.get_current_timezone())
>>> 'America/Sao_Paulo'def set_timezone(self,timezone:str)->bool:
Set the timezone for the lock mechanism. The timezone is used to calculate the expiration time of the lock. This method is called by the __init__(). It will only display messages if the debug parameter was enabled when creating the object.
>>> print(lock.set_timezone('America/Rio_Branco'))
25/05/11 04:44:19.983 [DEBUG] Time zone adjusted to 'America/Rio_Branco' (was 'UTC'). Now is 2025-05-11 04:44:19 -05 [0.000057 sec].
>>> Truedef warmup(self)->bool:
Warm up the lock table to check if it is available and working. This method is called by the __init__() method and should return True or can be disabled by setting the 'warmup' parameter to False when creating the object. It will only display messages if the verbose and/or debug parameters were enabled when creating the object.
>>> print(lock.warmup())
25/05/11 04:44:20.495 [DEBUG] Warm-Up put_item 'warmup_lock_d1b06a37-0503-4c99-a095-48f3563bed25' (ttl 1746956661) on table 'ddblock' in 0.512620 sec.
25/05/11 04:44:20.645 [DEBUG] Warm-Up query on table 'ddblock' in 0.150209 sec.
25/05/11 04:44:20.799 [DEBUG] Warm-Up delete_item on table 'ddblock' in 0.153090 sec.
25/05/11 04:44:20.799 [INFO] Warm-Up finished in 0.512717 sec.
>>> Truedef acquire(self, force:bool=False, lock_ttl:int|None=None, retry_timeout:int|None=None, retry_interval:float|None=None)->DynamoDBLockAcquireReturnProxy:
Acquire the lock. If the lock is already acquired by another process, it will wait until the lock is released or the retry_timeout is reached. Use the 'force' parameter to acquire the lock by force, ignoring if the lock is already acquired by another process. By calling this method, you can also change the parameters provided during creation, such as lock_ttl, retry_timeout and retry_interval.
>>> lock.acquire(force=True)
25/05/11 04:44:21.113 [DEBUG] Lock 'mylock1' successfully acquired by force [0.165980 sec]def release(self,force:bool=False, raise_on_exception:bool=False)->bool:
Releases the lock and returns True if it was successfully completed. The lock is only released if the DynamoDB record actually belongs to this session, i.e., the lock_id, lock_region, owner_id and ttl must be equal to the values that are configured in the object's memory, otherwise the lock will not be released. If you use the force=True parameter, it unconditionally deletes the DynamoDB lock (use with caution).
>>> lock.release()
25/05/11 04:44:21.113 [DEBUG] The current lock 'mylock1' does not belong to this session... lock release aborted [0.165980 sec]
>>> False
>>> lock.release(force=True)
25/05/11 04:44:21.113 [DEBUG] Lock 'mylock1' successfully released by force [0.165980 sec]
>>> Truedef get_all_locks(self,order_by:Optional[Literal['lock_id','ttl','ttl_precise','owner_id']]='ttl_precise',reverse:bool=False)->List[dict]:
Lists all locks found in the given DynamoDB resource table. Has the option to sort by main fields ('lock_id','ttl','ttl_precise','owner_id'). The data is returned as a generator.
>>> for item in lock.get_all_locks(order_by='ttl_precise'):
... print(item)
25/05/14 05:31:02.962 [DEBUG] Started to scan all locks
{'lock_id': 'mylock1', 'ttl': Decimal('1747211471'), 'ttl_precise': Decimal('1747211471.9021206'), 'lock_region': 'us-east-1', 'owner_id': 'f32dbbf6', 'expire_datetime': datetime.datetime(2025, 5, 14, 5, 31, 11, 902121), 'expire_datestring': '2025-05-14 05:31:11.902121 -03'}
{'lock_id': 'mylock2', 'ttl': Decimal('1747211472'), 'ttl_precise': Decimal('1747211472.5237079'), 'lock_region': 'us-east-1', 'owner_id': '7b35d1ed', 'expire_datetime': datetime.datetime(2025, 5, 14, 5, 31, 12, 523708), 'expire_datestring': '2025-05-14 05:31:12.523708 -03'}
{'lock_id': 'mylock3', 'ttl': Decimal('1747211472'), 'ttl_precise': Decimal('1747211472.8167684'), 'lock_region': 'us-east-1', 'owner_id': 'f2eaeb34', 'expire_datetime': datetime.datetime(2025, 5, 14, 5, 31, 12, 816768), 'expire_datestring': '2025-05-14 05:31:12.816768 -03'}
25/05/14 05:31:03.107 [DEBUG] Scan all locks finished! [0.145813 sec]To return all the data in a list at once, call the function with the List type, otherwise it will be delivered item by item like a generator.
>>> all_locks = list(lock.get_all_locks(order_by=None)):
>>> print(all_locks)
[{'lock_id': 'mylock3', 'ttl': Decimal('1747212155'), 'ttl_precise': Decimal('1747212155.1342103'), 'lock_region': 'us-east-1', 'owner_id': '15d67fc3', 'expire_datetime': datetime.datetime(2025, 5, 14, 5, 42, 35, 134210), 'expire_datestring': '2025-05-14 05:42:35.134210 -03'}, {'lock_id': 'mylock1', 'ttl': Decimal('1747212154'), 'ttl_precise': Decimal('1747212154.1937928'), 'lock_region': 'us-east-1', 'owner_id': '8734726c', 'expire_datetime': datetime.datetime(2025, 5, 14, 5, 42, 34, 193793), 'expire_datestring': '2025-05-14 05:42:34.193793 -03'}, {'lock_id': 'mylock2', 'ttl': Decimal('1747212154'), 'ttl_precise': Decimal('1747212154.8239918'), 'lock_region': 'us-east-1', 'owner_id': '72de54c8', 'expire_datetime': datetime.datetime(2025, 5, 14, 5, 42, 34, 823992), 'expire_datestring': '2025-05-14 05:42:34.823992 -03'}]def release_all_locks(self)->List[dict]:
Delete all locks in the current DynamoDB table and return a list of dict with all released locks. Up until version 1.0.5, the release_all_locks() function returned a generator. Starting with version 1.0.6, you can simply call lock.release_all_locks() without any issues.
>>> print(lock.release_all_locks())
[{'lock_id': 'mylock1', 'ttl': Decimal('1747271472'), 'ttl_precise': Decimal('1747271472.042874'), 'lock_region': 'us-east-1', 'owner_id': '807d5f41', 'expire_datetime': datetime.datetime(2025, 5, 14, 22, 11, 12, 42874), 'expire_datestring': '2025-05-14 22:11:12.042874 -03'}]
>>> for released_lock in lock.release_all_locks():
... print(f"Deleted lock: {deleted_lock}")
25/05/14 05:50:00.608 [DEBUG] Started to release all locks
25/05/14 05:50:00.608 [DEBUG] Started to scan all locks
25/05/14 05:50:00.911 [DEBUG] Successfully released lock 'mylock1', ttl:1747212564, ttl_precise:1747212564.6625602, expire_datestring:2025-05-14 05:49:24.662560 -03, lock_region: us-east-1, owner_id:bd507158 [0.138907 sec]
Deleted lock: {'lock_id': 'mylock1', 'ttl': Decimal('1747212564'), 'ttl_precise': Decimal('1747212564.6625602'), 'lock_region': 'us-east-1', 'owner_id': 'bd507158', 'expire_datetime': datetime.datetime(2025, 5, 14, 5, 49, 24, 662560), 'expire_datestring': '2025-05-14 05:49:24.662560 -03'}
25/05/14 05:50:01.048 [DEBUG] Successfully released lock 'mylock2', ttl:1747212565, ttl_precise:1747212565.2897048, expire_datestring:2025-05-14 05:49:25.289705 -03, lock_region: us-east-1, owner_id:dafa8060 [0.136913 sec]
Deleted lock: {'lock_id': 'mylock2', 'ttl': Decimal('1747212565'), 'ttl_precise': Decimal('1747212565.2897048'), 'lock_region': 'us-east-1', 'owner_id': 'dafa8060', 'expire_datetime': datetime.datetime(2025, 5, 14, 5, 49, 25, 289705), 'expire_datestring': '2025-05-14 05:49:25.289705 -03'}
25/05/14 05:50:01.183 [DEBUG] Successfully released lock 'mylock3', ttl:1747212565, ttl_precise:1747212565.622608, expire_datestring:2025-05-14 05:49:25.622608 -03, lock_region: us-east-1, owner_id:e13c4c22 [0.135249 sec]
Deleted lock: {'lock_id': 'mylock3', 'ttl': Decimal('1747212565'), 'ttl_precise': Decimal('1747212565.622608'), 'lock_region': 'us-east-1', 'owner_id': 'e13c4c22', 'expire_datetime': datetime.datetime(2025, 5, 14, 5, 49, 25, 622608), 'expire_datestring': '2025-05-14 05:49:25.622608 -03'}
25/05/14 05:50:01.183 [DEBUG] Scan all locks finished! [0.575000 sec]
25/05/14 05:50:01.183 [DEBUG] Released 3 lock(s) from a total of 3 lock(s) [0.575048 sec]- When a Lambda function attempts to acquire the lock, it inserts an item in the table with a TTL (
time-to-live). - If another process already holds the lock and it hasn't expired, the new attempt is delayed.
- If the lock expires or is released, other processes may acquire it.
| Parameter | Type | Description |
|---|---|---|
lock_id |
str |
Unique lock ID |
dynamodb_table_resource |
boto3.Table |
DynamoDB table resource |
lock_ttl |
int |
Lock TTL (in seconds) |
retry_timeout |
float |
Total retry duration to acquire the lock |
retry_interval |
float |
Interval between retries |
owner_id |
str |
Owner identifier (e.g. context.aws_request_id) |
warmup |
bool |
Test table on init |
timezone |
str |
Timezone, e.g. UTC, America/Sao_Paulo |
verbose |
bool |
Enable logs |
debug |
bool |
Enable debug logs |
log_prefix |
str |
A text to be used as prefix in verbose or debug |
The library defines specific exceptions:
DynamoDBLockExceptionDynamoDBLockTimeoutErrorDynamoDBLockWarmUpExceptionDynamoDBLockAcquireExceptionDynamoDBLockReleaseExceptionDynamoDBLockGetLockExceptionDynamoDBLockCheckLockExceptionDynamoDBLockPutLockException
Creates a DynamoDB table intended to store locks, with flexible customization options. This function does not handle credentials or access keys, you need to provide an already instantiated boto3.client with your credentials data.
This function simplifies the creation of a DynamoDB table by predefining key parameters, but also supports several optional configurations via keyword arguments. The default behavior is to create a table with:
- Primary key: 'lock_id' (type 'S')
- Billing mode: 'PAY_PER_REQUEST'
- TTL (Time to Live) enabled on attribute 'ttl'
- Table class: 'STANDARD'
Optionally, you can provide a custom boto3 DynamoDB client. If not provided, a new client will be created using the specified region.
This function does not support the creation of local or global secondary indexes.
create_dynamodb_table(table_name:str, boto3_client:BaseClient, verbose:bool=True, raise_on_exception:bool=False, **kwargs)->bool:
Parameters:
table_name (str): The name of the DynamoDB table to be created.
boto3_client (BaseClient): An existing boto3 DynamoDB client.
verbose (bool, optional): If True, prints detailed progress and validation messages. Default is False.
raise_on_exception (bool, optional): If True, raises exceptions instead of returning False on failure. Default is False.
**kwargs: Additional parameters to customize table creation:
- key_name (str): Name of the primary key attribute. Default is 'lock_id'.
- key_type (str): Type of the key attribute. Default is 'S'.
- billing_mode (str): 'PAY_PER_REQUEST' or 'PROVISIONED'. Default is 'PAY_PER_REQUEST'.
- table_class (str): 'STANDARD' or 'STANDARD_INFREQUENT_ACCESS'. Default is 'STANDARD'.
- delete_protection (bool): Enable deletion protection. Default is False.
- read_capacity_units (int): Provisioned read capacity (if billing_mode is 'PROVISIONED').
- write_capacity_units (int): Provisioned write capacity (if billing_mode is 'PROVISIONED').
- max_read_requests (int): Optional On-Demand throughput configuration.
- max_write_requests (int): Optional On-Demand throughput configuration.
- read_units_per_second (int): Optional Warm throughput configuration.
- write_units_per_second (int): Optional Warm throughput configuration.
- stream_enabled (bool): Enable DynamoDB Streams. Default is True. Global Tables requires this parameter Enabled in all tables.
- stream_view_type (str): View type for streams ('NEW_IMAGE', 'OLD_IMAGE', 'NEW_AND_OLD_IMAGES', 'KEYS_ONLY').
- sse_enabled (bool): Enable server-side encryption. Default is False.
- sse_type (str): SSE type ('AES256' or 'KMS'). Default is 'AES256'.
- kms_master_key_id (str): Required if sse_type is 'KMS'. Must be a valid KMS key ID.
- resource_policy (str): Optional IAM resource policy as a JSON string.
- tags (list): List of tags in format [{'Key': ..., 'Value': ...}].
Returns:
bool: True if the table was successfully created (and TTL configured), False if failed and raise_on_exception is False.
Raises:
Exception: If raise_on_exception is True and any validation or AWS call fails, otherwise will return True or False.
Example:
>>> import boto3
>>> from dynamodblock import create_dynamodb_table
>>> your_previously_created_client = boto3.client('dynamodb',region_name='us-east-1',YOUR_CREDENTIALS...)
>>> create_dynamodb_table(
... table_name="my_lock_table",
... boto3_client=your_previously_created_client,
... billing_mode="PROVISIONED",
... read_capacity_units=5,
... write_capacity_units=5,
... verbose=True,
... raise_on_exception=True
... )Notes:
- You need to provide a valid boto3 DynamoDB client.
- To update TTL information on your new table may require retries while the table is still being created. Normally the total time does not exceed 10 seconds.
- For full API details:
* boto3 docs: https://boto3.amazonaws.com/v1/documentation/api/latest/reference/services/dynamodb/client/create_table.html
* AWS docs: https://docs.aws.amazon.com/amazondynamodb/latest/APIReference/API_CreateTable.html
Context manager to measure execution time:
with ElapsedTimer() as elapsed:
time.sleep(1)
print(elapsed.text(decimal_places=6,end_text=" sec",with_brackets=True)) # [1.000000 sec]Safe timeout decorator using multiprocessing:
@SafeTimeoutDecorator(timeout=5)
def slow_task():
...- Name: any
- Primary key:
lock_id(string) - TTL enabled on the
ttlattribute (UNIX timestamp)
{
"lock_id": "my-task-lock",
"ttl": 1715384400,
"ttl_precise": 1715384400.234555,
"lock_region": "us-east-1",
"owner_id": "abc123"
}- GitHub: github.com/rabuchaim/dynamodblock
- PyPI: pypi.org/project/dynamodblock
- Bugs / Issues: issues page
MIT License
Ricardo Abuchaim ([email protected]) - github.com/rabuchaim
Contributions, testing, ideas, or feedback are very welcome! 🌟