An esoteric programming language to play around and create boolean functions while being strictly limited to operations involving NAND gates.
The NAND gate is functionally complete. Thus, any boolean function (
Still, it is not a Turing-complete language. For example, while loops are not allowed.
To build the interpreter, you need to have dune installed.
cd src
dune build
cd ..
mv src/interpreter.exe .After building the interpreter, you can execute it on your .nand source file.
./interpreter.exe file.nandAs a convention, lowercase names are used for booleans, and uppercase names for arrays.
x = 1; /* Defines x as the boolean value 1 (true) */
x = 0; /* Changes the value of x to 0 (false) */
X{8} = 0; /* Defines X as an array of lenght 8 filled with 0 (false) */
X[2] = 1; /* Changes the value of X[2] to 1 (true) */
Using the same convention as for variables, lowercase names are used for functions returning booleans, and uppercase names for functions returning arrays.
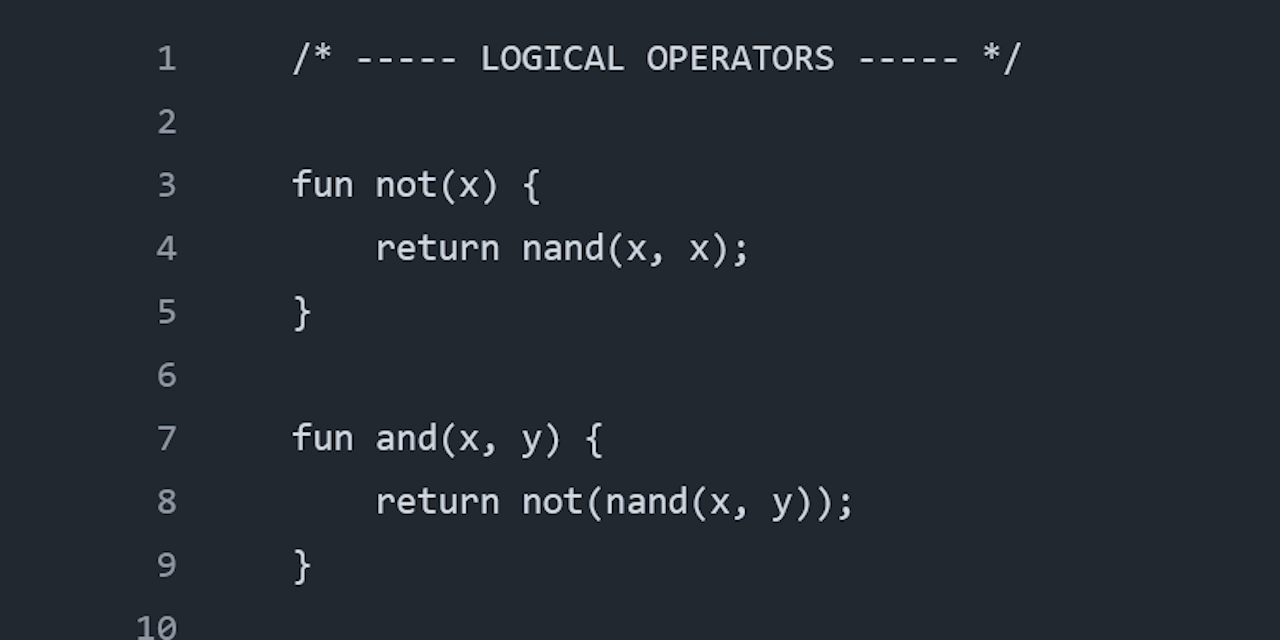
fun not(x) {
return nand(x, x); /* nand is the only already-defined function */
}
For loops can only iterate over a range of indices (inclusive).
for i = 0 to 3 {
X[i] = not(X[i]);
}
There are two debugging tools: debug print and debug [int32 | int16 | int8]
debug print X; /* Prints X as a human-readable value */
debug int8 X; /* Prints the 8-bit signed integer representation of X */
Here is a simple example:
fun not(x) {
return nand(x, x);
}
fun main() {
X{8} = 0;
X[2] = 1;
debug print X; /* Output: Array { Bool false Bool false Bool true Bool false Bool false Bool false Bool false Bool false } */
for i = 0 to 3 {
X[i] = not(X[i]);
}
debug print X; /* Output: Array { Bool true Bool true Bool false Bool true Bool false Bool false Bool false Bool false } */
debug int8 X; /* Output: Int8 11 */
}
A larger example code providing an implementation of 16-bits signed integers can be found in file.nand
Distributed under the MIT License. See LICENSE.md