-
Notifications
You must be signed in to change notification settings - Fork 0
Shared Memory Architecture
In the previous speedup example, we used OpenMP, an API for writing multithreaded applications.
An important note when designing high performance applications is that the parallel algorithm needs to effectively utilize the compute resources that derive from the memory architecture of the physical machine. OpenMP helps us effectively utilize the shared memory compute resources on the CPU by allowing us to tell the computer to "execute this part of the code in parallel." In essence, OpenMP is a parallel programming model for CPU parallel execution.
In order to facilitate the development of appropriate solutions on numerous system architectures, parallel programming models exist as an abstraction for expressing algorithms with respect to the hardware. There are several parallel programming models that are currently used HPC systems.
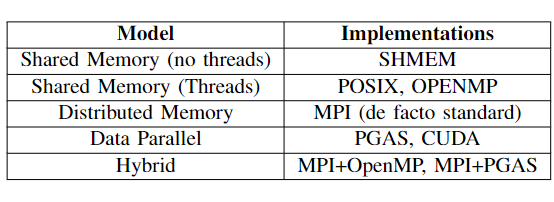
Both OpenMP and Kokkos are shared memory programming models designed for shared memory machines.
Shared memory machines are computers that are composed of multiple processing elements that share an address space. These are further divided into two classes:
- Symmetric multiprocessor (SMP): a shared address space with “equal-time” access for each processor, and the OS treats every processor the same way.
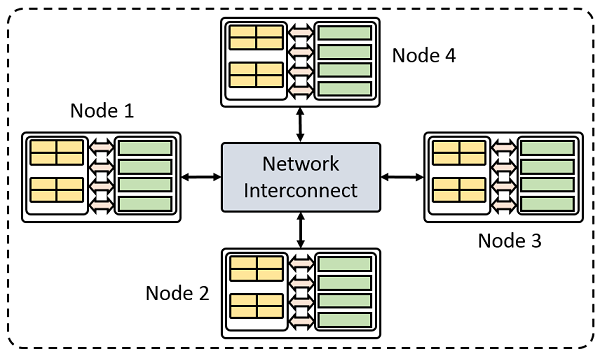
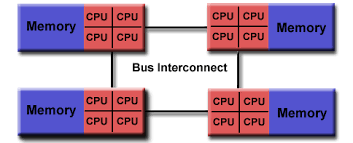
- Non Uniform address space multiprocessor (NUMA): different memory regions have different access costs … think of memory segmented into “Near” and “Far” memory
For this project, I ran my code on a NUMA shared memory compute node with two numa regions. You can view some of the machine specs and these numa regions from the Linux Shell Command lscpu as seen here
-
One process and lots of threads that communicate by sharing variables
-
Threads interact through reads/writes to a shared address space
-
OS scheduler decides when to run which threads
-
A race condition happens when the program's outcome changes as the threads are scheduled differently
-
Synchronization can be used to protect such conflicts and assure correct results, but it is expensive
-
Memory access patterns can be optimized to reduce the need for synchronization
Wiki
Fundamental Concepts
- What is HPC?
- How Do Computers Solve Problems?
- Serial to Parallel speedup example
- Shared Memory Architecture
- Heterogenous Architectures
Getting Started with Kokkos