-
Notifications
You must be signed in to change notification settings - Fork 0
Serial To Parallel Speedup Example
In this example we use OpenMP (an API for writing multi-threaded applications) in order to go from using one thread of CPU execution, to two threads of CPU execution. The goal of this example is to show how utilizing more cores of a CPU in parallel helps us solve problems faster.
CPU threads are the virtual components that divide the physical core of a CPU into virtual multiple cores. Recall from the previous section how multiple cores deliver the workload to the CPU more efficiently, as long as we tell the computer to run in parallel with something like OpenMP.
I use OpenMP in this example because Kokkos is a shared memory programming model, and it's very benefecial when writing/understanding Kokkos to also have a firm grasp on OpenMP shared-memory parallelism.
...
static long num_steps = 100000000;
start_time = omp_get_wtime();
for (i=1;i<= num_steps; i++){
x = (i-0.5)*step;
sum = sum + 4.0/(1.0+x*x);
}
pi = step * sum;
run_time = omp_get_wtime() - start_time;
} ...
#define NUM_THREADS 2
omp_set_num_threads(NUM_THREADS);
start_time = omp_get_wtime();
#pragma omp parallel for private(x) reduction(+:sum)
for (i=1;i<= num_steps; i++){
x = (i-0.5)*step;
sum = sum + 4.0/(1.0+x*x);
}
pi = step * sum;
run_time = omp_get_wtime() - start_time; Number of Physical Cores * Number of Threads per core = Number of Logical Cores
4 * 2 = 8
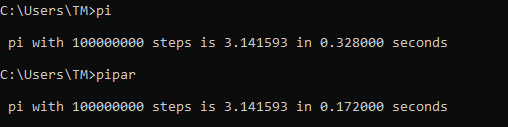
speedup = Serial / Parallel speed up = 1.90 (about twice as fast with 2 Threads as opposed to 1)
Wiki
Fundamental Concepts
- What is HPC?
- How Do Computers Solve Problems?
- Serial to Parallel speedup example
- Shared Memory Architecture
- Heterogenous Architectures
Getting Started with Kokkos